DELSY - Dubna Electron Synchrotron
The project DELSY is based on a unique accelerator complex of the Netherlands Institute of Nuclear and High-Energy Physics (NIKHEF, Amsterdam). It was transferred to the possession of JINR free of charge. The complex comprises:
- a 800-MeV linear electron accelerator,
- a 950-MeV electron storage synchrotron,
- a beam line to transport the linear accelerator beam to the storage ring,
- power supply, cooling and control systems and devices.
The NIKHEF linear accelerator, the so-called Medium Energy Accelerator (MEA), was designed by the Haimson Research Corporation (USA) in 1969-1974, built in 1975-78, and commissioned in 1978. It is analogous to the famous Stanford Two Miles Accelerator in the United States.
The electron storage ring, the NIKHEF electron synchrotron, was built in the early 1990s to stretch (to increase the duration of) electron current pulses in the linear stacker (hence its name the Amsterdam Pulse Stretcher, AmPS). Later AmPS served to store polarized electrons for nuclear-physics experiments. The AmPS beam parameters are such that it cannot be used as a high-intensity SR source. However, the AmPS design allows a new high-intensity source to be built on its basis, which is to be done within the framework of the DELSY project.
The total cost of the equipment passed to JINR from NIKHEF is over US$ 25,000,000.
JINR is an international intergovernmental organization comprising 18 member states. Two countries collaborate with JINR on the basis of agreements between the governments (so-called associate members).
Dubna is a unique place for wide international collaboration. It has accumulated great intellectual potential and gained good experience in setting up international research teams. The Institute and the town developed an intellectual milieu that is solely inherent in large scientific centers and allows several-fold acceleration of scientific investigations.
An important activity intimately related to construction of a new basic facility in JINR and organization of corresponding research is training of students and specialists, which can be carried out in JINR Education Centre, Moscow State University and its Dubna Branch of the Institute of Nuclear Physics, Dubna International University "Nature, Society, Man", and Pushchino University.
It is also important that JINR has a well-developed social infrastructure providing comfortable conditions for a long stay of scientists who come to work at Dubna. Neither Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics nor Kurchatov Institute is able to provide similar conditions.
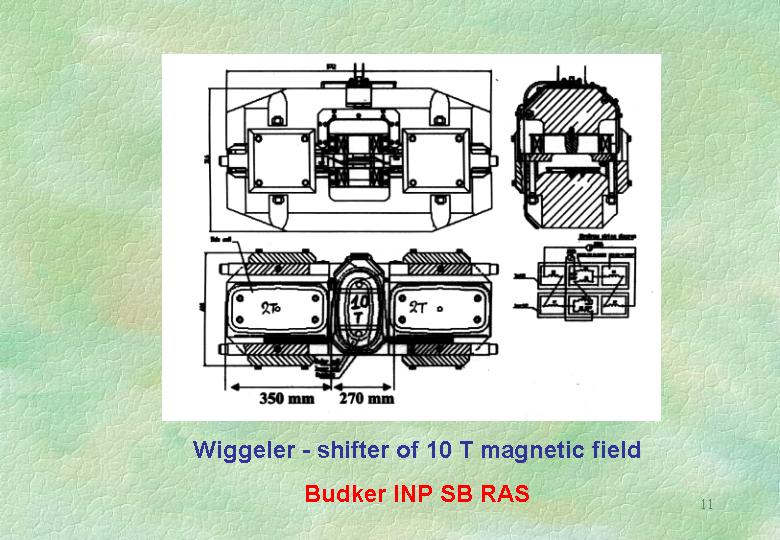
Actually JINR has two next buildings for the DELSY allocation: the building #118 has a length of 200 m and is well suitable for the linear electron accelerator and the building #119 (65 m x 35 m) could be reconstruct for the mounting of accumulation ring and experimental stations. These buildings have virtually everything to ensure appropriate power supply for DELSY. Additional equipment (undulator and superconducting wiggler) will be manufactured at the Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics under the most favorable conditions.
The existed infrastructure sufficiently reduces all principal expenditures for implementation of DELSY at JINR.
Prior to putting the accelerator complex into operation, experimental stations of the first phase for SR experiments must be built. It is planned that their equipment will be designed and manufactured at organizations of the JINR member states. According to estimates, the cost of equipment for the stations will eventually amount to a few million of US dollars.
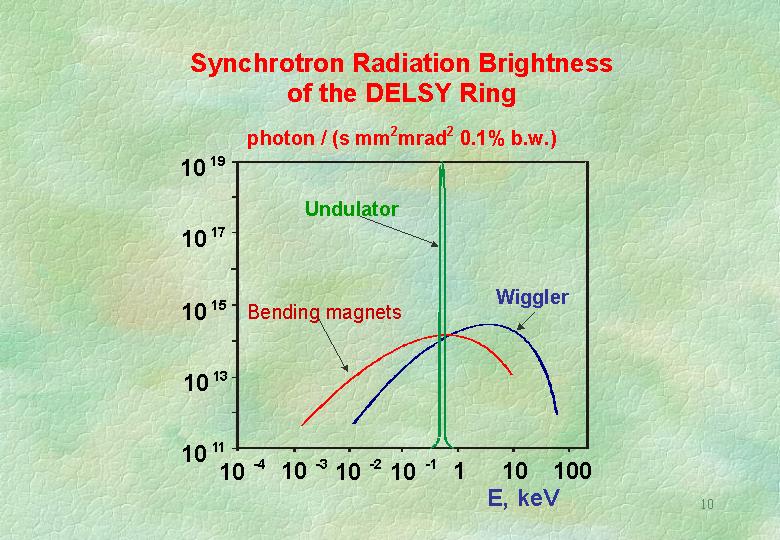
On implementation of DELSY the electron energy in the storage ring will increase to 1.2 GeV and the storage ring luminosity will increase by three orders of magnitude owing to an improved beam focussing circuit developed at JINR. Insertion devices (wigglers and undulators) will drastically increase the scope of the DELSY storage ring. All these features of the storage ring allow its parameters to match the current level of third-generation SR sources.
It is important that with its parameters DELSY will complement and extend the potentialities of the synchrotron source Sibir-2 in the Russian Scientific Center "Kurchatov Institute". Long co-operation between our institutes will allow us to work by a common research programme in the future.
The DELSY linear electron accelerator Linac-800 can be used to create free-electron lasers (FEL). The design of this accelerator provides a beam branch in the energy range from 20 to 140 MeV. The extracted beam in this energy range can be used to generate infrared and ultraviolet FEL radiation with wavelengths from 300 mm to 200 nm. The beam of maximum energy up to 800 MeV will allow an FEL with the wavelength below 5 nm. The first stage in implementing the project DELSY will include upgrading and mounting of the linear accelerator and construction of beam extraction lines for free-electron lasers.
Construction of a synchrotron radiation center is of great interest for many JINR member states. Institutes of Belarus, Kazakhstan, Russia, Romania, Ukraine, and Czech Republic submitted their proposals for investigations at DELSY. In November 1999 and April 2001 JINR had held two special workshops to discuss the DELSY research program. All leading scientific centers of the JINR member states engaged in SR research participated in the workshop. The Memorandum signed by the participants definitely expresses importance and necessity of realizing this project as soon as possible. A specialized MSU-JINR Research Training Center of Synchrotron Radiation is organized now.
Implementation of the project DELSY will give impetus to formation of SR users community in Russia and CIS, a community working under a coordinated program founded on potentialities of all SR centers in Russia. This in turn will promote SR research in these centers.
Construction of a third-generation SR source in Dubna will considerably enrich the JINR research program. The new field will considerably extend the current experimental potentialities of JINR, first of all in condensed matter physics: in addition to its unique neutron source IBR-2, JINR will get an SR source.
For many years JINR has been involved in treating tumor patients with the so-called medical beams form the Phasotron. On 1 December 1999 a special hospital was opened for such patients. With an SR source, treatment will be supplemented with prompt high-resolution X-ray diagnosis.
The scientific program of JINR is approved by the Scientific Council, whose members are eminent scientists from physics institutes of the world. The JINR budget is made of contributions from member states and associate members. It is approved by the Committee of Plenipotentiaries of the Member States annually. The JINR program of activities adopted for the coming years does not allow financing of the DELSY project from the Institute's budget. The JINR Directorate seeks the possibility of attracting funds of interested organizations in Russia and in JINR member states.
Implementation of the project DELSY will result in the first SR source of the third generation in Russia, which will stop our country's falling behind in this promising field and will ensure a breakthrough in fundamental research and high technologies
Analysis of the accelerator equipment transferred from Amsterdam to Dubna has shown that it has a significant operating resource and can be used for many years in the future at an appropriate change of auxiliary equipment. An appropriate upgrade of the equipment it would become possible to build in Dubna a universal light source with unique characteristics consisting of the following components and stages:
Phase I.
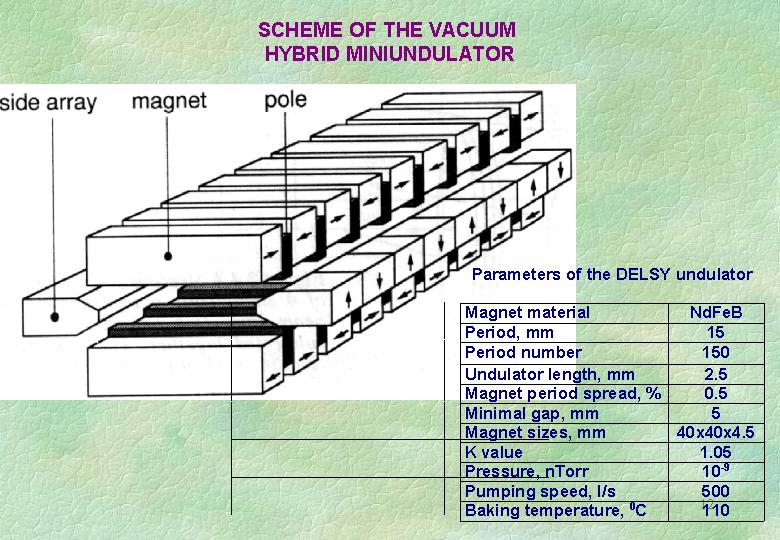
Undulator specification for the DELSY project
Type
Period, cm Peak magn. field, T Gap, cm Number of periods Total length, cm FEL Parameter list for the DELSY project
Parameter Electron energy, MeV Radiation wavelength, mm Bunch charge, nC Peak current, A Bunch length, mm Norm. emittance, mm.mrad Energy spread, keV
Micropulse repet. rate, MHz
Macropulse duration, ms Repetition rate, Hz A complex of FELs covering continuously the wavelength range from far- infrared (150 µm) down to UV (150 nm) and far-infrared coherent radiation source capable of generating high-power radiation (up to 100 MW peak and up to 50 W average) in the wavelength range from 150 nm up to 1 mm;
Phase II. DELSY storage ring (1.2 GeV SR source of 3rd generation with photon energy up to 50 keV);
Phase III. VUV/soft X-ray FEL with minimal wavelength down to 1 A - Self Amplified Spontaneous Emission (SASE) FEL. 4. Elaboration of the DELSY project.
The work began in 1999. By June 2000 the entire NIKHEF acceleration complex was disassembled by the JINR specialists and brought to Dubna. This work was paid by a long-term credit granted by the Holland side. The expenditures for disassembling and transportation up to date are in the limits of preliminary and tentative estimations of cost. The State Specialized Institute for Design (SSID) started to design buildings and engineering structures for DELSY (including upgrading of the existing linear accelerator building).
Phase 1 will be accomplished with the construction of a complex of FELs covering continuously the spectrum from FIR down to UV. The FIR coherent source will cover continuously the submillimeter wavelength range. Realization of this phase will not require a significant modification of the JINR infrastructure, and all the accelerator equipment and user facility can be mounted inside existing buildings. Even the first stage of the project will result in a unique user facility in the world. None of the present facilities is able to produce in one place such a wide spectrum of coherent radiation.
Realization of this stage will make it possible to establish a universal laser centre with a unique range of smooth radiation tuning.
A summary of the radiation properties from coherent radiation sources being planned in Phase 1 is presented in Table. Notations G1-G4 refer to the FEL, and FIR stands for the FIR coherent source.
Status (January 2002):
o Technical project of Linac-800 assembling is completed
o Conceptual project of short bunch formation and acceleration in the Linac-800 is elaborated
o Building #118 reparation for Linac-800 is in progress
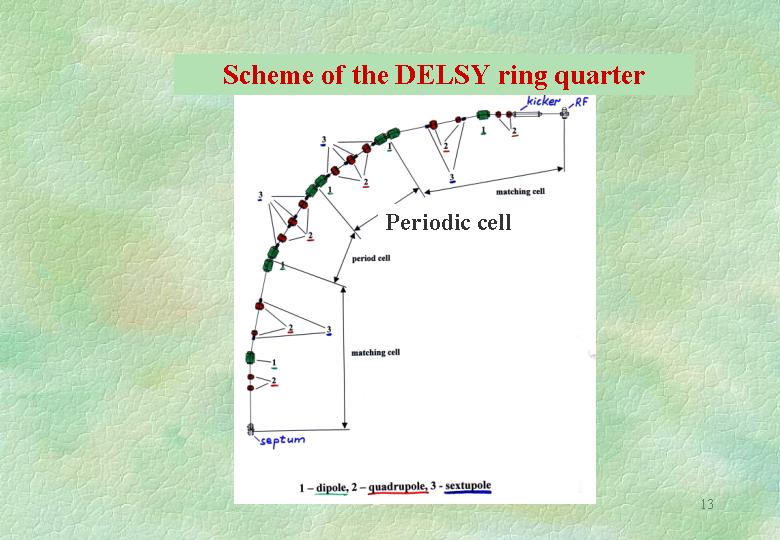
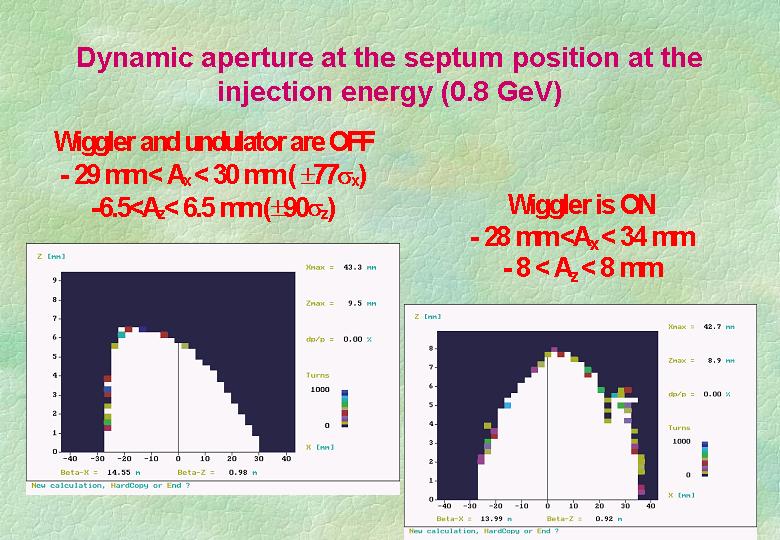
o New concept of the ring layout is proposed
Plans for 2002:
o Beginning of the Linac-800 assembling and bringing into operation its injector-buncher
o Elaboration of technical project of the ring construction (reconstruction of building #119, tunnel, infrastructure, etc.)