

Next: Conclusion
Up: Manual
Previous: Blurring and enhancing
Using the LIFTPACK software package [6], we implement a WALF
program aimed to filter one-dimensional signals.
WALF provides an user-friendly Graphical User Interface (GUI) which makes
it quite easy to use.
GUI is implemented based on some of the ROOT [7] classes.
So, WALF requires ROOT to be installed first.
However, WALF classes, that are not related to visualization or GUI,
are ROOT-independent.
In this user's guide we show how to work with WALF (version 1.0) using GUI.
To get started, just type walf in your command line (WALF is to be
installed, of course).
The WALF main window (see Fig. 1) appearers.
Fig. 2:
Read-out and view options dialogs
|
|
Fig. 3:
Thresholding and blurring/enhancing dialogs
|
|
The following features are implemented in WALF program:
- File menu
- Open
- Open a new data file.
Data file (ASCII) should contain at least one column with a data set.
In this case this column is taken as a signal to be filtered.
Otherwise, the first column in the data file is interpreted as x-axis
samples, the second one -- as a signal.
This can be changed by read-out options (see below).
- Add
- Open a data file and draw its data without clearing
the pad.
(This allows one to superimpose two graphs.)
- Re-open
- Open the same data file again.
(When read-out options are unchanged it looks like just an UNDO option.)
- Save image
- Save the image in a choosen format.
EPS format is default. PS and GIF formats are also possible.
- Dump ASCII
- Save the filtered signal to ASCII file.
The first column in it will contain x-axis samples, the second one --
filtered signal samples and the third -- differences between the
filtered signal and the original one.
- Exit
- Exit WALF program.
- Option menu
- Read option
- Set read-out options.
By default, the first column in the data file is interpreted as x-axis
samples, the second one - as a signal.
(If the data file contains one column only, it is taken as a signal, and
naturals -- as x-axis samples.)
One can change this by read option dialog (Fig. 2, left).
- View option
- Set view options
(linear or logarithmic scales, grids, title and axis labels)
using view option dialog (Fig. 2, right).
- Tools menu
- Threshold
- Filter a signal using a thresholding dialog
(Fig. 3, left).
The histogram in the thresholding window upper part presents a
scalogram:
its
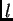 's bin-content is given by
's bin-content is given by
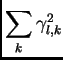 ,
where
,
where 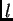 is the level number.
The scalogram is interpreted as an energy distribution over signal
frequencies.
It often helps to separate signal components with different frequencies
(e.g., extract the noise from the main signal).
Move a slider down to cut the corresponding frequency level off
(the threshold value is set over a space above the slider).
is the level number.
The scalogram is interpreted as an energy distribution over signal
frequencies.
It often helps to separate signal components with different frequencies
(e.g., extract the noise from the main signal).
Move a slider down to cut the corresponding frequency level off
(the threshold value is set over a space above the slider).
- Enhance
- Filter a signal using blurring/enhancing dialog
(Fig. 3, right).
User can choose a factor
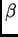 to multiply wavelet coefficients
at a level by it.
Note, that factors for higher levels would be calculated automatically
(ones for lower levels would be unchanged).
If
to multiply wavelet coefficients
at a level by it.
Note, that factors for higher levels would be calculated automatically
(ones for lower levels would be unchanged).
If 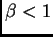 , then the level is blurred.
If
, then the level is blurred.
If 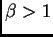 , then the level is enhanced.
, then the level is enhanced.
- Help menu
Show this help.
Some of these features a duplicated as buttons in the main window.
As an example, fig. 1 shows a signal, which is a sine wave
contaminated by Gaussian white noise.
The bold line is a filtered signal, obtained from it by cutting high
frequencies off.


Next: Conclusion
Up: Manual
Previous: Blurring and enhancing
Soloviev Alexei
2002-04-15
![\includegraphics[width=120mm]{fig/e10-2001-___/MainFrame.eps}](img31.png)
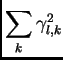 ,
where
,
where