- Introduction
JINR participates in the CMS project in the framework of the
Russia and Dubna Member States (RDMS) CMS collaboration.
- RUSSIA AND DUBNA MEMBER STATES CMS COLLABORATION (RDMS
CMS)
Groups of scientists representing scientific institutes of
Russia and Dubna member states that are organized efficiently as
the RDMS collaboration are an important part of the CMS
collaboration [2].
Fig. 2 shows the composition of the RDMS collaboration.
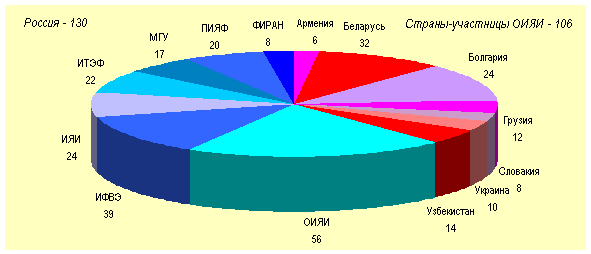
Fig. 2: Composition of the Russia and Dubna member
states CMS collaboration.
292 scientists affiliated with 21 institutes of 8 countries
participate in RDMS. In particular, JINR, seven Dubna member
states, and six Russian institutes are represented by 56, 106, and
130 scientists, respectively. Apart of that, a few groups
totalling 21 scientists affiliated with two Russian institutes are
the associated members of the CMS collaboration.
- CMS DISCOVERY POTENTIAL
Extensive studies have been undertaken to optimise the set-up.
In particular, detailed simulation of the CMS detector response
has been performed [1,7].
The objective of these efforts is to investigate if the detector
is adequate to the above extraordinary problems.
- RUSSIA AND DUBNA MEMBER STATES PARTICIPATION IN THE
CONSTRUCTION OF THE CMS DETECTOR
The major JINR efforts on the design, optimisation and
construction of the set-up are concentrated on the end cap hadron
calorimeters (HE), forward muon stations ME1/1, for which RDMS
bears a full responsibility, and on the participation in the
construction of the silicon strip detectors for the preshower
detector of the electromagnetic calorimeter (SE).
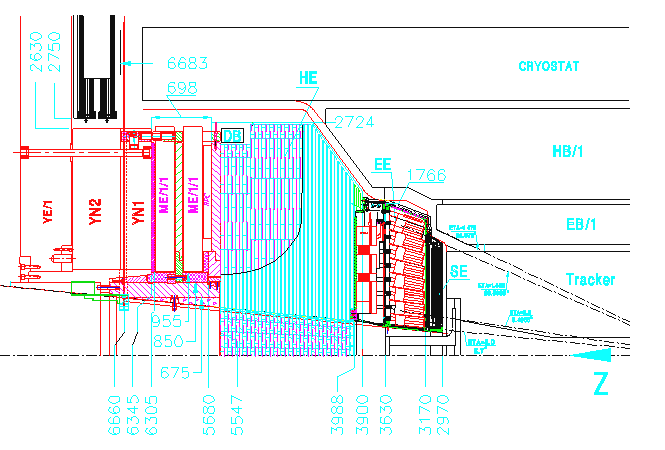
Fig. 3: Layout of the CMS endcap detectors. The HE/YE
interface serve to suspend the endcap detectors SE, EE, HE, and
ME1/1 whose total weight is 300 ton on the iron disk of the
return yoke. Deformations and stresses from the weight and
magnetic field force are decreased by the sliding joint between
HE backflange and interface tube, and by a rigid joint on the
outer edge by brackets with enlarged strength properties.
The results of numerous prototypes have shown that the
performance of the detectors meet requirements of the experiment.
The completion of the design of HE, ME1/1, and SE, and the
integration of the endcap detectors (Fig. 3) has become major
accomplishments of the last years. These projects [4,
5,
6]
have been successfully defended. Approval of the designs gives the
green light for the manufacturing of the mechanisms of the endcap
hadron calorimeters, chambers of the forward muon stations, and
the silicon detectors. This is a rather important stage of the
work that has culminated the research and development stage, and
initiated mass production of the detector under the construction
schedule of the CMS detector.