 |
||
|
||||||||
| Part 1 | up |
|
Arbuzov A.B., Bytev V.V., Kuraev E.A., Tomasi-Gustafsson E., Bystritskiy Yu.M. Exact Results in QED (eng, 755 Kb) This review is devoted to exact calculations of cross sections of QED processes in relativistic approach. We consider the case when the velocity of final heavy particles is not particularly close to the speed of light. Especially, the cases of muon radiative pair creation are considered. In the framework of QED with pion form factor, we estimate the pion radiative pair creation. All leading terms are included in the framework of structure function approach. The annihilation of electron-positron to the hadronic final state with one additional tagged photon is considered. The radiative corrections are calculated, and the numerical estimation is made. Target spin asymmetry and charge asymmetry are investigated for e 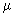 -scattering processes.
Initial-state radiation (returning to resonance) mechanism is
investigated including radiative corrections to initial and final states.
Possible method of experimental extraction of the ratio of electric and magnetic
form factors of a proton is suggested for different processes in lepton--proton scattering.
Some useful algebraic relations and integrals are~presented. -scattering processes.
Initial-state radiation (returning to resonance) mechanism is
investigated including radiative corrections to initial and final states.
Possible method of experimental extraction of the ratio of electric and magnetic
form factors of a proton is suggested for different processes in lepton--proton scattering.
Some useful algebraic relations and integrals are~presented.
|
|
|
Arbuzov A.B., Bytev V.V., Kuraev E.A., Tomasi-Gustafsson E., Bystritskiy Yu.M. Processes with Heavy-Ion Collisions (eng, 483 Kb) Some Coulomb effects in heavy-ion collisions are considered. Among them are the process of muon- and lepton-pair creation, Coulomb and unitary corrections, statistics of multiple pair production. Effects of multiple photon exchange in process of lepton pair production by linearly polarized photon on nuclei are considered. This process is used for measuring the polarization of initial photon. Relativistic muon energy loss due to the light lepton pair production in the Coulomb field are calculated. Also we consider the effects of multiple photon exchange in elastic lepton scattering on unscreened atomic field and discuss the possible experimental testing. |
|
|
Arbuzov A.B., Bytev V.V., Kuraev E.A., Tomasi-Gustafsson E., Bystritskiy Yu.M. Some QED Processes: Light-by-Light and M 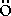 ller Scattering (eng, 272 Kb) ller Scattering (eng, 272 Kb) Some Coulomb effects in heavy-ion collisions are considered. Among them are the process of muon- and lepton-pair creation, Coulomb and unitary corrections, statistics of multiple pair production. Effects of multiple photon exchange in process of lepton pair production by linearly polarized photon on nuclei are considered. This process is used for measuring the polarization of initial photon. Relativistic muon energy loss due to the light lepton pair production in the Coulomb field are calculated. Also we consider the effects of multiple photon exchange in elastic lepton scattering on unscreened atomic field and discuss the possible experimental testing. |
|
|
Chizhov M.V. Theory and Phenomenology of Spin-1 Chiral Particles (rus, 2.173 Mb) We consider all finite representations of the Lorentz group and their association with spin properties of the particles. It is shown that for given nontrivial spin there exist several nonequivalent representations differing by chirality, which in a massless case correspond to different particles with different helicities. Spin-1 case, which includes standard field description by the vector-potential and nonstandard one by the second rank antisymmetric tensor field, is considered in detail. The first field transforms under real representation (1/2,1/2), while the second field transforms under chiral representations (1,0) and (0,1). On an example of spin-1 hadron resonances it is shown that these two fields describe two different types of particles existing in Nature. The given idea is used further for the Standard Model extention by the new type of spin-1 chiral particles. Its phenomenological consequences are studied in detail. |
|
|
Synopsis (rus, 49 Kb) |
|
| Part 2 | up |
|
Balin D.V., Ganzha V.A., Kozlov S.M., Maev E.M., Petrov G.E.,
Soroka M.A., Schapkin G.N., Semenchuk G.G., Trofimov V.A., Vasiliev A.A.,
Vorobyov A.A., Voropaev N.I., Petitjean C., Gartner B.,
Lauss B., Marton J., Zmeskal J., Case T., Crowe K.M., Kammel P.,
Hartmann F.J., Faifman M.P. High Precision Study of Muon Catalyzed Fusion in D2 and HD Gases (eng, 2.995 Mb) Muon catalyzed dd fusion in D2 and HD gases in the temperature range from 28 to 350 K was investigated in a series of experiments based on a time-projection ionization chamber operating with pure hydrogen. The final analysis of the data together with a comprehensive comparison with calculations based on recent 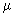 CF theory are
presented in this work.
All main characteristics of the chain of accompanying reactions
including the resonant and nonresonant dd CF theory are
presented in this work.
All main characteristics of the chain of accompanying reactions
including the resonant and nonresonant dd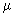 formation rates, the
rate for hyperfine transitions in d formation rates, the
rate for hyperfine transitions in d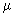 atoms, the branching ratio of
the two charge symmetric fusion channels 3He + n and t + p and the
muon sticking probability were extracted from data measured with high
absolute precision. The obtained energy atoms, the branching ratio of
the two charge symmetric fusion channels 3He + n and t + p and the
muon sticking probability were extracted from data measured with high
absolute precision. The obtained energy 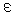 11(fit) = -1.9651(7)eV
of the loosely bound dd 11(fit) = -1.9651(7)eV
of the loosely bound dd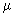 molecule state responsible
for the high rate of resonant molecule formation is in impressive
agreement with the latest theoretical results molecule state responsible
for the high rate of resonant molecule formation is in impressive
agreement with the latest theoretical results
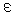 11(theory) = -1.9646 eV. 11(theory) = -1.9646 eV.
|
|
|
Pshenichnov I.A. Electromagnetic Excitation and Fragmentation of Ultrarelativistic Nuclei (rus, 1.379 Mb) Electromagnetic interactions of high-energy nuclei in ultraperipheral collisions are investigated. Such collisions, which take place without any overlap of nuclear densities, can be considered as irradiation of nuclei by intense photon beams with a wide energy spectrum. This leads to several unusual phenomena, namely mutual electromagnetic excitation of nuclei including exotic double and triple excitations of giant resonances, as well as multifragmentation of nuclei. The RELDIS model is presented, which describes fragmentation of nuclei and meson production by equivalent photons. It is shown that RHIC and LHC colliders provide unique possibilities to study electromagnetic interactions of ultrarelativitic nuclei. Cross sections calculated by the RELDIS model are used as input for the method to monitor LHC luminosity and in simulating interactions of beam nuclei with LHC construction elements. |
|
|
Dubovichenko S.B., Uzikov Yu.N. Astrophysical S-Factors of Reactions with Light Atomic Nuclei (rus, 2.238 Mb) Two-cluster model constitutes a phenomenological semi-microscopic approach to study many-nucleon systems. Within this model, interaction of the nucleon clusters is described by local potential determined by fit to the scattering data and properties of bound states of these clusters. Many-body character of the problem is taken into account under some approximation, in terms of the two-cluster bound states generated by this interaction potential and separated according to the Pauli principle into allowed or forbidden states of the full system of the nucleons. An important feature of the approach is accounting for a dependence of interaction potential between clusters on the orbital Young scheme, which determines the permutation symmetry of the nucleon system. Photonuclear processes in the p2H, p3H, p6Li, p12C, as well as 4He12C, 3He4He, 3H4He, 2H4He systems and corresponding astrophysical S-factors are analyzed in this review on the basis of this approach. It is shown that the approach allows one to describe quite reasonably experimental data available at low energies, especially for systems with number of nucleons A > 4 for the cases in which the phase shifts of cluster-cluster scattering are extracted from the data with minimal errors. |
|
|
Kiselev M.A. Methods for Investigation of Lipid Nanostructures at Neutron and Synchrotron Sources (rus, 2.316 Mb) Lipid membrane is a major component of the biological membrane. Phospholipids and ceramides are basic components of drugs and cosmetics in the modern bionanotechnologies. Phospholipids nanoparticles are used as drug carriers. Development of bionanotechnolgó in Russia is urgency and requires the development of diagnostic methods for nanoparticles, which are prospective for pharmacology application. Radiations with a wavelength of 1-10 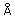 are
appropriate instrument for examination of the bilayer and monolayer of lipids.
Review of methods of application of the neutron and synchrotron radiations
is presented for the case of nanostructure investigation of the lipid
bilayer, phospholipid nanoparticles, phospholipid monolayer on the water
substrate via methods of diffraction, small-angle scattering, and
reflectometry. The importance of complementary application of neutron and
synchrotron radiation is demonstrated as the specific study of phospholipid
membranes and membranes based on the ceramides for the decision of hot
topics in the membrane biophysics, microbiology, dermapharmacology, and
bionanotechnology. The efficiency of development and application of
new methods for the decision of separate problems of current
importance in biophysics is demonstrated.
The review presents the main results obtained from 1999 to 2010 in
Frank Laboratory of Neutron Physics, JINR in the collaboration with
Pharmaceutical Faculties of Paris-Sud University (Chatenay Malabry, France)
and Martin Luther University (Halle, Germany). are
appropriate instrument for examination of the bilayer and monolayer of lipids.
Review of methods of application of the neutron and synchrotron radiations
is presented for the case of nanostructure investigation of the lipid
bilayer, phospholipid nanoparticles, phospholipid monolayer on the water
substrate via methods of diffraction, small-angle scattering, and
reflectometry. The importance of complementary application of neutron and
synchrotron radiation is demonstrated as the specific study of phospholipid
membranes and membranes based on the ceramides for the decision of hot
topics in the membrane biophysics, microbiology, dermapharmacology, and
bionanotechnology. The efficiency of development and application of
new methods for the decision of separate problems of current
importance in biophysics is demonstrated.
The review presents the main results obtained from 1999 to 2010 in
Frank Laboratory of Neutron Physics, JINR in the collaboration with
Pharmaceutical Faculties of Paris-Sud University (Chatenay Malabry, France)
and Martin Luther University (Halle, Germany).
|
|
|
Frontasyeva M.V. Neutron Activation Analysis in the Life Sciences (rus, 2.185 Mb) The development of instrumental neutron activation analysis and its application in the Life Sciences are reviewed. A special emphasis is made on the epithermal activation with reactor neutrons (ENAA), and the advantages of this method for the analysis of the environmental samples are demonstrated. A review of investigations in Life Sciences carried out by means of ENAA at the world's leading nuclear centers is given. Experience in applying activation analysis with epithermal neutrons to environmental studies using analytical complex at the reactor IBR-2 of FLNP, JINR, is summarized. |
|
|
Synopsis (rus, 69 Kb) |
|
| Part 3 | up |
|
Dineykhan M., Zhaugasheva S.A. Determination of the Mass Spectrum of a Bound State in the Framework of Relativistic Hamiltonian Approach (rus, 0.585 Mb) We propose one of the versions of calculation of the energy spectrum of bound state systems with relativistic corrections. In the framework of quantum field theory the expression that takes into account relativistic corrections to the mass of the bound state with a known nonrelativistic pair interaction potential is proposed on the basis of calculating the asymptotic behaviour of correlation functions of the corresponding field currents with the necessary quantum numbers. Excluding the time variables allows one to determine nonperturbative corrections to the interaction potential. In the framework of the given approach the following results are obtained. The nonperturbative corrections arising due to the relativistic nature of a system to the interaction Hamiltonian are determined. The dependence of the constituent mass, of bound-state forming particles, on the free state mass and on the orbital and radial quantum numbers is analytically derived. The energy level shift of muonic hydrogen taking into account relativistic corrections is calculated. The energy spectrum of wide class of potentials, which describe the Coulomb bound state, is analytically derived with relativistic corrections. The mass spectrum of the glueballs and the constituent masses of the gluons are analytically calculated taking into account spin-orbit, spin-spin and tensor interactions. Our numerical results have shown very good agreement with the lattice data. Taking into account nonperturbative and nonlocality characters of interactions, the mass spectrum of the mesons consisting of the light-light and light-heavy quarks with orbital and radial excitations is determined. Our results show that good agreement with the experimental data for the slope and the intercept of the Regge trajectory can be obtained only taking into account the nonperturbative and the nonlocal characters of interactions. Dependence of the constituent masses of constituent particles on the masses of a free state is certain. When quarks are light, the difference of current and valent masses of quarks is greater than valent masses of quarks, and when quarks are heavy the difference of these masses is insignificant. One of the alternative variants of the accounting of nonlocality is suggested for the definition of properties of hadrons at large distances. The dependence of the constituent masses of constituent particles on the radius of confinement is determined. |
|
|
Khvedelidze A.M. Hamiltonian Reduction of SU(2) Gluodynamics (rus, 0.576 Mb) The Hamiltonian reduction of Yang-Mills theory with the structure group SU(2) to a nonlocal model of self-interacting 3 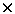 3 positive semidefinite matrix field is presented.
Analysis of the field's transformation properties under the
Poincare group action is given.
It is shown that in the limit of a strong coupling
the classical dynamics of the reduced system
can be described within the local theory of interacting
nonrelativistic
spin-0 and spin-2 fields.
A perturbation theory in powers of the inverse coupling constant g-2/3,
which
allows one to calculate corrections to the leading
long-wave approximation, is suggested. 3 positive semidefinite matrix field is presented.
Analysis of the field's transformation properties under the
Poincare group action is given.
It is shown that in the limit of a strong coupling
the classical dynamics of the reduced system
can be described within the local theory of interacting
nonrelativistic
spin-0 and spin-2 fields.
A perturbation theory in powers of the inverse coupling constant g-2/3,
which
allows one to calculate corrections to the leading
long-wave approximation, is suggested.
|
|
|
Batusov V.Yu., Lyablin M.V., Topilin N.D. The Development and Application of Hardware-Software for the Controlled Assembly of ATLAS Hadron Tile Calorimeter (rus, 2.153 Mb) The article contains developed by the authors hardware-software complex and geometry control methods of the main constituent elements and final assembly of the hadron tile calorimeter. The developed complex was used at all stages of the calorimeter creation and allowed one to reach high-design precision when creating the world largest research ATLAS spectrometer. |
|
|
Yukalov V.I. Basics of Bose-Einstein Condensation (eng, 0.635 Mb) The review is devoted to the elucidation of the basic problems arising in the theoretical investigation of systems with Bose-Einstein condensate. Understanding these challenging problems is necessary for the correct description of Bose-condensed systems. The principal problems considered in the review are as follows: (i) What is the relation between Bose-Einstein condensation and global gauge symmetry breaking? (ii) How to resolve the Hohenberg-Martin dilemma of conserving versus gapless theories? (iii) How to describe Bose-condensed systems in strong spatially random potentials? (iv) Whether thermodynamically anomalous fluctuations in Bose systems are admissible? (v) How to create nonground-state condensates? Detailed answers to these questions are given in the review. As examples of nonequilibrium condensates, three cases are described: coherent modes, turbulent superfluids, and heterophase fluids. |
|
|
Synopsis (rus, 60 Kb) |
|
| Part 4 | up |
| Proceedings of the IV International Pontecorvo Neutrino Physics School (Alushta, Crimea, Ukraine, September 26 - October 6, 2010) | |
|
Preface (eng, 24 Kb) |
|
|
Bilenky S.M. On the Theory of Neutrino Mixing and Oscillations (eng, 0.296 Mb) |
|
|
Wojcicki S.G. Accelerator Neutrino Physics - Current Status and Future Prospects (eng, 4.507 Mb) |
|
|
Poutissou J.-M. Status of the T2K Experiment (eng, 0.398 Mb) |
|
|
Gornushkin Yu.A. Search for  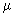 
  Oscillations in Appearance Mode
in the OPERA Experiment (eng, 1.088 Mb)
Oscillations in Appearance Mode
in the OPERA Experiment (eng, 1.088 Mb) |
|
|
Chen M.C. Solar Neutrino Experiments: Status and Prospects (eng, 0.321 Mb) |
|
|
Grimus W. Theory of Neutrino Masses and Mixing (eng, 0.310 Mb) |
|
|
Gonzalez-Garcia M.C. Neutrinos: Determination of Masses and Mixing (eng, 0.774 Mb) |
|
Th mmler T. (for the KATRIN Collaboration) mmler T. (for the KATRIN Collaboration)Direct Neutrino Mass Measurements (eng, 0.693 Mb) |
|
 imkovic F. imkovic F.Neutrinoless Double-Beta Decay and Related Topics (eng, 1.509 Mb) |
|
|
Barabash A.S. Double-Beta Decay Experiments (eng, 3.815 Mb) |
|
|
Pastor S. Light Neutrinos in Cosmology (eng, 0.618 Mb) |
|
|
Fornengo N. Dark Matter: Theory (eng, 1.012 Mb) |
|
|
Rau W. Dark Matter Search Experiments (eng, 0.536 Mb) |
|
|
Potzel W. M  ossbauer Antineutrinos: Recoilless Resonant Emission and
Absorption of Electron Antineutrinos (eng, 0.221 Mb) ossbauer Antineutrinos: Recoilless Resonant Emission and
Absorption of Electron Antineutrinos (eng, 0.221 Mb) |
|
|
Mezzetto M. Future Neutrino Long Baseline Experiments (eng, 0.955 Mb) |
|
|
Bolshakova A. (for the HARD-CDP Group) There Any «LSND Anomaly»? (eng, 0.955 Mb) |
|
| Part 5 | up |
|
Popov Yu.V., Zaytsev S.A., Vinitsky S.I. J-Matrix Method of Calculations of Three-Body Coulomb Wave Functions and Cross Sections of Physical Processes (rus, 0.625 Mb) The review is devoted to widely known method of a numerical solution of the three-body Coulomb problem, namely the J-matrix method. The special attention is focused on the ways of solution of the integral Lippmann-Schwinger equation without attraction of pseudostates. There are revealed difficulties connected with a formulation of the integral equation in the spherical coordinates, which lead to a divergence of its integral part if one calculates the wave function with two asymptotically free electrons. The relation between exact and approximate solutions remains unclear, when the matrix of a residual potential is restricted to a finite number of basis functions, and this number goes up. It is shown that, in principle, these problems can be avoided by reformulating them in the parabolic coordinates. |
|
|
Borisov G.I. Theoretical and Experimental Physical Methods of Neutron Capture Therapy (rus, 28.100 Mb) The framework of this review is formed mainly by our priority IR-8 NRC «Kurchatov Institute» reactor - based research and development. New NCT theoretical and experimental methods are developed and practically applied. - General analytic and semi-empirical NCT theory based on classical neutron physics: elementary deceleration theory, diffusion, reflection and absorption of neutrons, and not on mathematical simulation. The theory is intended first of all for practical implementation by physicists, engineers, biologists and physicians. This theory could be completely mastered basing on practically general higher education. - Methods of phantom experimental research for semi-empirical NCT theory on intermediate neutrons. - Experimental measuring and control methods of spectral composition of therapeutic, research and analytical neutron beams. - Experimental methods of remote neutron dosimeter of biological objects with intentionally modified tissue elementary composition. - Methods of mass examinations of pharmacokinetics of biological efficiency of novel dose-forming preparations. - Methods of therapeutic, research and analytical neutron beams tailoring. - Methods of capillary neutron optics applications for NCT and other fundamental and applied neutron research. |
|
|
Zobov M. (on behalf of DAÔNE, SuperB and SuperC-Tau Accelerator Teams) New Generation Electron-Positron Factories (eng, 3.364 Mb) In 2010 we celebrated 50 years since commissioning of the first particle-storage ring ADA in Frascati (Italy) that also became the first electron-positron collider in 1964. After that date, the particle colliders have increased their intensity, luminosity, and energy by several orders of magnitude. Namely, because of the high stored beam currents and high rate of useful physics events (luminosity) the modern electron-positron colliders are called «factories». However, the fundamental physics has required luminosities by 1-2 orders of magnitude higher with respect to those presently achieved. This task can be accomplished by designing a new generation of factories exploiting the potential of a new collision scheme based on the Crab Waist (CW) collision concept recently proposed and successfully tested in Frascati. In this paper we discuss the performance and limitations of the present generation electron-positron factories and give a brief overview of new ideas and collision schemes proposed for further collider luminosity increase. In more detail, we describe the CW collision concept and the results of the crab waist collision tests in DA  NE, the Italian NE, the Italian 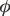 -factory. Finally, we briefly describe most
advanced projects of the next-generation factories based on the CW concept:
SuperB in Italy, SuperKEKB in Japan, and SuperC-Tau in Russia. -factory. Finally, we briefly describe most
advanced projects of the next-generation factories based on the CW concept:
SuperB in Italy, SuperKEKB in Japan, and SuperC-Tau in Russia.
|
|
|
Boya L.J., Rivera C. On the Masses of Elementary Particles (eng, 0.233 Mb) We make an attempt to describe the spectrum of masses of elementary particles, as it comes out empirically in six distinct scales. We argue for some rather well-defined mass scales, like the electron mass; we elaborate on the assumption that there is a minimum mass associated to any electric charge. Another natural mass scale is 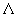 = = 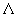 QCD coming arbitrarily
at quantizing a classically conformal SU(3)c theory. Indeed, some scales of masses
will cover also masses of composite particles or mass differences. We extend some plausible
arguments for other scales, as binding or self-energy effects of the microscopic
forces, plus some speculative uses, here and there, of gravitation. We also
consider briefly exotics like supersymmetry and extra dimensions in
relation to the mass scale problem, including some mathematical arguments (e.g., triality),
which might throw light on the three-generation problem. We also address briefly the issues
of dark matter and dark energy. The paper is rather tentative and speculative and does not make
many predictions, but it aims to explain some features of the particle spectrum. QCD coming arbitrarily
at quantizing a classically conformal SU(3)c theory. Indeed, some scales of masses
will cover also masses of composite particles or mass differences. We extend some plausible
arguments for other scales, as binding or self-energy effects of the microscopic
forces, plus some speculative uses, here and there, of gravitation. We also
consider briefly exotics like supersymmetry and extra dimensions in
relation to the mass scale problem, including some mathematical arguments (e.g., triality),
which might throw light on the three-generation problem. We also address briefly the issues
of dark matter and dark energy. The paper is rather tentative and speculative and does not make
many predictions, but it aims to explain some features of the particle spectrum.
|
|
|
Tsyganov Yu.S. The Dubna Gas-Filled Recoil Separator: Program Products and Algorithms (rus, 11.225 Mb) The Dubna Gas-Filled Recoil Separator recent experiments performed at FLNR (JINR) confirmed the hypothesis of superheavy element island of stability existence. Success of those experiments was achieved due to the sum of techniques related with the accelerator and beam diagnostics, as well as the detection ones. Namely, with the separator detection system which can operate using the «active correlations» technique it has become possible to detect rare decays of superheavy nuclei in the background free mode. On the other hand, this detection procedure was successful due to specific algorithms and program products application in the long-term experiments with 48Ca projectiles. |
|
|
Synopsis (rus, 64 Kb) |
|
| Part 6 | up |
|
Ibraeva E.T., Zhusupov M.A., Imambekov O., Sakhyev S.K. Investigation of a Structure of Light Non-Stable Nuclei and Mechanism of Proton Elastic Scattering (rus, 7.286 Mb) The review provides calculations of elastic p6Íå-, p8Li-, p9Li-, and p9Ñ scattering within Glauber's theory of multiple diffraction scattering at intermediate energies of 70 and 700 MeV/nucleon. Noticeable feature of the calculations is that we have utilized realistic three-body wave functions obtained within modern nuclear models. There has been established the relation between differential cross-sections and intercluster potentials where wave functions of the nuclei were calculated. Conclusions on the types of potentials with the most realistic description of the whole range of experimental data are made. The method for calculation of three-body wave functions in 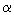 -n-n-, -n-n-,
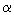 -t-n-, 7Be-p-p-, -t-n-, 7Be-p-p-,
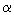 -t-2n- in
7Li-n-n models is described and intercluster potentials and various
configurations of quantum numbers are discussed. It is shown how the choice
of intercluster potentials influences wave functions and electromagnetic characteristics of nuclei calculated with
such wave functions. Within
Glauber's approach with three particle wave functions, our derivation of
matrix elements (amplitudes) of pA scattering is presented on example of
6Íå nucleus. Discussion on differential sections and analyzing power
(Ay describes how the calculated characteristics are dependent on wave
function structure and on dynamics of the process determined by Glauber's
multiple scattering operator. Comparison of calculated differential sections
and analyzing power with available experimental data and calculations by
other authors has been performed for various formalisms making us possible
to verify our conclusions. -t-2n- in
7Li-n-n models is described and intercluster potentials and various
configurations of quantum numbers are discussed. It is shown how the choice
of intercluster potentials influences wave functions and electromagnetic characteristics of nuclei calculated with
such wave functions. Within
Glauber's approach with three particle wave functions, our derivation of
matrix elements (amplitudes) of pA scattering is presented on example of
6Íå nucleus. Discussion on differential sections and analyzing power
(Ay describes how the calculated characteristics are dependent on wave
function structure and on dynamics of the process determined by Glauber's
multiple scattering operator. Comparison of calculated differential sections
and analyzing power with available experimental data and calculations by
other authors has been performed for various formalisms making us possible
to verify our conclusions.
|
|
|
Rodionov V.N., Kravtsova G.A. The Energy Level Shifts, Wave Functions and the Probability Current Distributions for the Bound Scalar and Spinor Particles Moving in a Uniform Magnetic Field (eng, 0.475 Mb) We discuss the equations for the bound one-active electron states based on the analytic solutions of the Schr 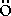 dinger
and Pauli equations for a uniform magnetic field and a single
attractive dinger
and Pauli equations for a uniform magnetic field and a single
attractive 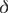 (r) potential. We show that the magnetic
field indeed plays a stabilizing role in considered systems in the
case of the weak intensity, but the opposite occurs in the case
of strong intensity. These properties may be important for real
quantum mechanical fermionic systems in two and three dimensions.
In addition, we obtained that including the spin in the framework
of the nonrelativistic approach allows correctly taking the effect
of the magnetic field on the electric current into account. (r) potential. We show that the magnetic
field indeed plays a stabilizing role in considered systems in the
case of the weak intensity, but the opposite occurs in the case
of strong intensity. These properties may be important for real
quantum mechanical fermionic systems in two and three dimensions.
In addition, we obtained that including the spin in the framework
of the nonrelativistic approach allows correctly taking the effect
of the magnetic field on the electric current into account.
|
|
|
Kondratiev V.P., Feofilov G.A. Strange Particles Production in Relativistic Heavy-Ion Collisions (rus, 5.128 Mb) This review mainly covers data on the strange particle production in Pb+Pb collisions obtained in heavy ion experiments at CERN SPS. K, 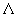 , ,
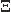 and and  yields are considered as well as their rapidity and
transverse mass distributions depending on the centrality of Pb+Pb
collisions at SPS energies. Experimental results are compared with the
predictions of the statistical model of nuclear fireball and the microscopic
parton-string model. We discuss in detail the experimentally observed effect
of strangeness enhancement in nucleus-nucleus collisions compared to the
nucleon-nuclear interactions and its interpretation within the various
theoretical models. We analyze also the behavior of hyperon yields and
nuclear modification factors from SPS to RHIC energies. yields are considered as well as their rapidity and
transverse mass distributions depending on the centrality of Pb+Pb
collisions at SPS energies. Experimental results are compared with the
predictions of the statistical model of nuclear fireball and the microscopic
parton-string model. We discuss in detail the experimentally observed effect
of strangeness enhancement in nucleus-nucleus collisions compared to the
nucleon-nuclear interactions and its interpretation within the various
theoretical models. We analyze also the behavior of hyperon yields and
nuclear modification factors from SPS to RHIC energies.
|
|
|
Izosimov I.N., Kalinnikov V.G., Solnyshkin A.A. Fine Structure of the Strength Functions for the Beta-Decay of Atomic Nuclei (rus, 2.063 Mb) The 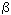 -decay strength function
S -decay strength function
S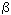 (E) is a distribution of the modules
squared of the (E) is a distribution of the modules
squared of the 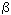 -decay-type matrix elements in nuclear excitation
energies E. The S -decay-type matrix elements in nuclear excitation
energies E. The S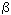 (E)
defines the characteristics of (E)
defines the characteristics of 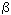 decay, spectra of
radiation accompanying the decay, spectra of
radiation accompanying the 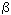 decay,
and probabilities of delayed processes following the decay,
and probabilities of delayed processes following the 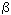 decay.
Until recently total absorption decay.
Until recently total absorption
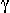 spectrometers and total absorption spectrometers and total absorption
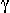 rays spectroscopy (TAGS) having low energy
resolution were used for experimental studies of the
S rays spectroscopy (TAGS) having low energy
resolution were used for experimental studies of the
S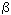 (E) structure.
Development of experimental technique allows application of methods of nuclear spectroscopy with high energy resolution
for studying S (E) structure.
Development of experimental technique allows application of methods of nuclear spectroscopy with high energy resolution
for studying S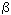 (E) fine structure. The most thorough study was performed for a series of nuclei produced on
a YASNAPP-2 complex in Dubna.
In this review the S (E) fine structure. The most thorough study was performed for a series of nuclei produced on
a YASNAPP-2 complex in Dubna.
In this review the S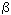 (E) fine structure research in spherical and deformed nuclei was analyzed.
The use of modern methods of nuclear spectroscopy allowed us to detect splitting of peaks in
S (E) fine structure research in spherical and deformed nuclei was analyzed.
The use of modern methods of nuclear spectroscopy allowed us to detect splitting of peaks in
S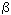 (E)
for the Gamow-Teller (GT) transitions in deformed nuclei. This splitting can be associated with anisotropy
of oscillation of the isovector nuclear density component. The resonance nature of
S (E)
for the Gamow-Teller (GT) transitions in deformed nuclei. This splitting can be associated with anisotropy
of oscillation of the isovector nuclear density component. The resonance nature of
S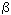 (E) for the
first-forbidden (E) for the
first-forbidden 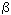 transitions (FF transitions) for both spherical and deformed nuclei was proved experimentally.
It was shown that at some values of excitation energy in nuclei the intensities of FF transitions can be comparable with
those of GT transitions. Criteria for testing the completeness nuclear decay schemes were considered. The
S transitions (FF transitions) for both spherical and deformed nuclei was proved experimentally.
It was shown that at some values of excitation energy in nuclei the intensities of FF transitions can be comparable with
those of GT transitions. Criteria for testing the completeness nuclear decay schemes were considered. The
S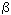 (E)
obtained by the TAGS method and those obtained with the use of high-resolution spectroscopy were compared. (E)
obtained by the TAGS method and those obtained with the use of high-resolution spectroscopy were compared.
|
|
|
Boreyko A.V., Krasavin E.A. Mutagenic Effect of Accelerated Heavy Ions on Bacterial Cells (rus, 1.049 Mb) With the use of heavy-ion accelerators of the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, regularities and mechanisms of the formation of mutations of different types in prokaryote cells were studied. Induction of direct mutations (lac-, tonB-, and colB) in Escherichia coli cells and reverse his- 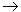 His+ mutations in
Salmonella typhimurium and Bacillus subtilis
cells under radiations in a wide range of linear energy transfer (LET) was investigated.
A comparative study was performed of the regularities in the formation of gene and structural
(tonB trp-) mutations in Escherichia coli bacteria under the effect of accelerated heavy
ions. It is shown that the dose dependences of gene mutation formation under
gamma quanta and accelerated heavy ions are described by linear quadratic
functions. Linear dose-effect dependences are typical of structural
mutations. The quadratic character of mutagenesis curves is caused by the
interaction of two mutually independent «hitting» events in the course of
the SOS repair of genetic structure damage. A conclusion is made that under
accelerated heavy ions, gene mutations are induced in the delta-electron
region of charged particle tracks. With the SOS chromotest, SOS lux test,
and lambda prophage induction, regularities in cell SOS response under
radiations in a wide LET range were studied. A thesis is substantiated that
clustered single-strand DNA breaks are the molecular basis of the gene
mutations, and DNA double-strand breaks are the molecular basis of
structural mutations. It is found that the LET dependence of the relative
biological effectiveness of accelerated ions is described by curves with a
local maximum. It is shown that the biological effectiveness of ionizing
radiations with different physical characteristics for cells with different
genotypes, evaluated by the lethal effect, gene and deletion mutation
induction, and the precise excision of transposons, is determined by the
specifics of radiation energy transfer, which influence the character of the
induced DNA damage, and by the efficiency of inducible and constitutive
systems of cell repair. An increase in the relative biological effectiveness
of heavy charged particles is determined by an increase in the yield of DNA
damage participating in the formation of the radiation-induced effects and
by the growth of the efficiency of the inducible repair systems. It is
established that the LET value (Lmax), at which the maximal values of
the RBE coefficients are observed against the used irradiation criteria, varies
depending on the character of the detected radiation-induced effect. It
is shown that for the gene mutations and induction of the precise excision
of the mobile elements, the Lmax values are found at about 20 keV/ His+ mutations in
Salmonella typhimurium and Bacillus subtilis
cells under radiations in a wide range of linear energy transfer (LET) was investigated.
A comparative study was performed of the regularities in the formation of gene and structural
(tonB trp-) mutations in Escherichia coli bacteria under the effect of accelerated heavy
ions. It is shown that the dose dependences of gene mutation formation under
gamma quanta and accelerated heavy ions are described by linear quadratic
functions. Linear dose-effect dependences are typical of structural
mutations. The quadratic character of mutagenesis curves is caused by the
interaction of two mutually independent «hitting» events in the course of
the SOS repair of genetic structure damage. A conclusion is made that under
accelerated heavy ions, gene mutations are induced in the delta-electron
region of charged particle tracks. With the SOS chromotest, SOS lux test,
and lambda prophage induction, regularities in cell SOS response under
radiations in a wide LET range were studied. A thesis is substantiated that
clustered single-strand DNA breaks are the molecular basis of the gene
mutations, and DNA double-strand breaks are the molecular basis of
structural mutations. It is found that the LET dependence of the relative
biological effectiveness of accelerated ions is described by curves with a
local maximum. It is shown that the biological effectiveness of ionizing
radiations with different physical characteristics for cells with different
genotypes, evaluated by the lethal effect, gene and deletion mutation
induction, and the precise excision of transposons, is determined by the
specifics of radiation energy transfer, which influence the character of the
induced DNA damage, and by the efficiency of inducible and constitutive
systems of cell repair. An increase in the relative biological effectiveness
of heavy charged particles is determined by an increase in the yield of DNA
damage participating in the formation of the radiation-induced effects and
by the growth of the efficiency of the inducible repair systems. It is
established that the LET value (Lmax), at which the maximal values of
the RBE coefficients are observed against the used irradiation criteria, varies
depending on the character of the detected radiation-induced effect. It
is shown that for the gene mutations and induction of the precise excision
of the mobile elements, the Lmax values are found at about 20 keV/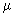 m.
For the lethal effects of irradiation and deletion mutation induction,
the Lmax values are about 50 and 100 keV/ m.
For the lethal effects of irradiation and deletion mutation induction,
the Lmax values are about 50 and 100 keV/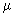 m, respectively. The
differences in the Lmax location for the studied radiation genetic
effects are determined by different types of DNA lesions involved in the
mutation process. A molecular model of gene mutations in Escherichia coli cells under
ionizing radiations is proposed. Within the framework of the model, the
basic types of DNA damage and the main ways of their repair are examined.
The model is based on the idea that the mutagenic branch of SOS repair,
which is error-prone, plays the decisive role in fixing the premutation DNA
lesions as point mutations. It is shown that the central mechanism of this
process consists in the formation of an inducible multienzyme complex,
which includes (UmuD'2C) DNA polymerase V, RecA protease, SSB proteins,
and a DNA polymerase III subunit. The complex performs erroneous DNA
synthesis on the damaged matrix. Based on the molecular model, a
mathematical model of gene mutation induction under ultraviolet irradiation
of cells was developed. m, respectively. The
differences in the Lmax location for the studied radiation genetic
effects are determined by different types of DNA lesions involved in the
mutation process. A molecular model of gene mutations in Escherichia coli cells under
ionizing radiations is proposed. Within the framework of the model, the
basic types of DNA damage and the main ways of their repair are examined.
The model is based on the idea that the mutagenic branch of SOS repair,
which is error-prone, plays the decisive role in fixing the premutation DNA
lesions as point mutations. It is shown that the central mechanism of this
process consists in the formation of an inducible multienzyme complex,
which includes (UmuD'2C) DNA polymerase V, RecA protease, SSB proteins,
and a DNA polymerase III subunit. The complex performs erroneous DNA
synthesis on the damaged matrix. Based on the molecular model, a
mathematical model of gene mutation induction under ultraviolet irradiation
of cells was developed.
|
|
|
Synopsis (rus, 80 Kb) |
|
| Author index (rus) | |
|
Subject index (rus) |