| 2014 |
|
E6-2014-1 (304.756)
Zvara I.
Vacuum Thermochromatography:
Physical Principles and Monte Carlo Simulation
The title method for preparative separation of infinitesimal amounts of
relatively volatile elements or compounds with different adsorbability is
based on the molecular flow in an evacuated open column with imposed
temperature gradient. The analytes put into the column's closed "hot" end
begin to migrate owing to random flights of their molecules between two
consecutive collisions with the wall. Each strike results in adsorption of
the entity on the surface for a random time whose mean increases
"downstream"; as a result, various analytes come to practical rest in
individual temperature ranges. Here, the microscopic picture of the
molecular histories is described in quantitative details, assuming that the
velocity vectors of the desorbing molecules obey the cosine law angular
distribution. The probability density functions for the full and projected
flight lengths in long cylinders are derived. They were used in Monte Carlo
simulation of great many migration histories to obtain the peaking profiles
of the deposits. Numerous particular sets of experimental regimes and
conditions were simulated to elucidate influence of these variables on the
profiles and the characteristic deposition temperatures.
|
P15-2014-2 (1.771.534)
Didyk A.Yu., Wi niewski R. niewski R.
Synthesis of Microparticles in Molecular Hydrogen at 1 kbar Pressure in Nuclear Reactions
Induced by Braking  -Rays of 10 MeV Threshold Energy. The Chemical Composition and
Structures at the Inner Surfaces of the Pressure Chamber Components -Rays of 10 MeV Threshold Energy. The Chemical Composition and
Structures at the Inner Surfaces of the Pressure Chamber Components
A high-pressure chamber filled with molecular hydrogen at 1 kbar was exposed
to braking  -rays produced by 10 MeV electron beam of 20-21 -rays produced by 10 MeV electron beam of 20-21  A
intensity during 14 h. Post-irradiation investigations of the structure
and elemental composition of the irregularities at the surface, as well as
of two largest synthesized particles among the ones registered after the
irradiation, established the presence of light elements from carbon to
calcium. Besides, multiple lead particles of small size were found and
studied. The detected synthesized particles have a complex shape and
composition. At the both sides of the inner surfaces of the cut brass sleeve,
thin-walled microtubes and other objects of complex shape were found. The
observed anomalies are discussed based on the models of the fusion of
hydrogen nuclei and heavier nuclei («upstream» reactions) and fission
reactions («downstream» reactions) and fusion reactions («upstream» reactions)
of nuclei in the chamber walls. A
intensity during 14 h. Post-irradiation investigations of the structure
and elemental composition of the irregularities at the surface, as well as
of two largest synthesized particles among the ones registered after the
irradiation, established the presence of light elements from carbon to
calcium. Besides, multiple lead particles of small size were found and
studied. The detected synthesized particles have a complex shape and
composition. At the both sides of the inner surfaces of the cut brass sleeve,
thin-walled microtubes and other objects of complex shape were found. The
observed anomalies are discussed based on the models of the fusion of
hydrogen nuclei and heavier nuclei («upstream» reactions) and fission
reactions («downstream» reactions) and fusion reactions («upstream» reactions)
of nuclei in the chamber walls.
|
P15-2014-3 (6.053.115)
Didyk A.Yu., Wi niewski R. niewski R.
Synthesis of Microparticles in Molecular Hydrogen at 1 kbar Pressure in Nuclear Reactions
Induced by Braking  -Rays of 10 MeV Threshold Energy. The Chemical Composition of the
Synthesized Particles and Structures
at the Surface of the Reaction Chamber -Rays of 10 MeV Threshold Energy. The Chemical Composition of the
Synthesized Particles and Structures
at the Surface of the Reaction Chamber
A chamber filled with molecular hydrogen at 1 kbar pressure was exposed to
braking  -rays with a threshold energy of 10 MeV produced by an
electron beam of 20-21 -rays with a threshold energy of 10 MeV produced by an
electron beam of 20-21  A intensity during 14 h. The studies of the
changes in the structure and element composition of the entrance window,
manganin foil, and collector of reaction products are presented in paper
[1]. This paper provides a discussion of the results of a study of the
synthesized particles and different formations at the inner surfaces of the
cut-in-half irradiation chamber (brass sleeve). The studies of the two
largest synthesized structures observed after irradiation established the
presence of light elements from carbon to calcium. As in [1], multiple lead particles of small size were observed and studied.
The detected synthesized particles have a complex shape and composition. At
both sides of the inner surfaces of the cut brass sleeve, thin-walled
microtubes were observed, as in [1]. The new elements and
structures are discussed on the basis of the upstream (fusion) and
downstream (fission) models of nuclear reactions (see [1]). A intensity during 14 h. The studies of the
changes in the structure and element composition of the entrance window,
manganin foil, and collector of reaction products are presented in paper
[1]. This paper provides a discussion of the results of a study of the
synthesized particles and different formations at the inner surfaces of the
cut-in-half irradiation chamber (brass sleeve). The studies of the two
largest synthesized structures observed after irradiation established the
presence of light elements from carbon to calcium. As in [1], multiple lead particles of small size were observed and studied.
The detected synthesized particles have a complex shape and composition. At
both sides of the inner surfaces of the cut brass sleeve, thin-walled
microtubes were observed, as in [1]. The new elements and
structures are discussed on the basis of the upstream (fusion) and
downstream (fission) models of nuclear reactions (see [1]).
|
005_2014_JINR_2013_Report_RAS (290.525)
|
P15-2014-6 (1.666.041)
Didyk A.Yu., Wi niewski R. niewski R.
Synthesis of New Structures on the Surface of a Pd-Rod
and HHPC Elements and Their Chemical Composition under Nuclear Reactions
Induced by Braking  -Rays with a Threshold Energy of 10 MeV
in Molecular Hydrogen at 0.5 kbar Pressure -Rays with a Threshold Energy of 10 MeV
in Molecular Hydrogen at 0.5 kbar Pressure
A high-pressure chamber filled with molecular hydrogen (HHPC) at 0.5 kbar
pressure, with a Pd-rod inside, was exposed during 14 hours to braking
 -rays with a threshold energy of 10 MeV produced by an electron
beam of 20-21 -rays with a threshold energy of 10 MeV produced by an electron
beam of 20-21  A intensity. The studies of the changes in the structure and
element composition of the Pd-rod and irregularities of all the internal
surfaces of the HHPC elements, as well as large synthetic structures
detected after irradiation, established the presence in them of light
elements from carbon to calcium. Besides that, multiple small-sized
particles of lead were also found and studied. The detected synthesized
particle has a complex shape and composition. Also, thin-walled micro tubes
were registered on the inner surfaces inside the HHPC. An attempt is made to
explain the observed anomalies based on fission reactions of intermediate
mass (downstream reactions) and reactions of fusion of elements from
hydrogen and heavier nuclei (upstream reactions). A intensity. The studies of the changes in the structure and
element composition of the Pd-rod and irregularities of all the internal
surfaces of the HHPC elements, as well as large synthetic structures
detected after irradiation, established the presence in them of light
elements from carbon to calcium. Besides that, multiple small-sized
particles of lead were also found and studied. The detected synthesized
particle has a complex shape and composition. Also, thin-walled micro tubes
were registered on the inner surfaces inside the HHPC. An attempt is made to
explain the observed anomalies based on fission reactions of intermediate
mass (downstream reactions) and reactions of fusion of elements from
hydrogen and heavier nuclei (upstream reactions).
|
P15-2014-7 (987.080)
Didyk A.Yu., Wi niewski R. niewski R.
Chemical Composition and Structure of the Synthesized Particles on
the Surface HHPC by Nuclear Reactions during Irradiation Brake
 -Rays with a Threshold Energy of 10 MeV in Molecular Hydrogen
at 0.5 kbar Pressure -Rays with a Threshold Energy of 10 MeV in Molecular Hydrogen
at 0.5 kbar Pressure
A chamber filled with molecular hydrogen at 0.5 kbar pressure (HHPC) with Pd-rod
inside was exposed to braking  -rays with a threshold energy
of 10 MeV produced by an electron beam of 20-21 -rays with a threshold energy
of 10 MeV produced by an electron beam of 20-21  A intensity during
14 hours.
The studies of the changes in the structure and element composition of the
synthesized particles and other objects on the surface of the brass sleeve,
an HHPC component, which were detected after irradiation,
established the presence in them of
light elements from carbon to calcium. Besides that, multiple
small-sized particles of lead were also found and studied.
The registered synthesized particles have a complex
shape and composition. At the inner surfaces of the HHPC thin-walled
microtubes were found. An attempt is made to explain
the observed anomalies basing on fission
reactions of intermediate mass (downstream reactions) and reactions of fusion
of elements from hydrogen and heavier nuclei (upstream reactions). A intensity during
14 hours.
The studies of the changes in the structure and element composition of the
synthesized particles and other objects on the surface of the brass sleeve,
an HHPC component, which were detected after irradiation,
established the presence in them of
light elements from carbon to calcium. Besides that, multiple
small-sized particles of lead were also found and studied.
The registered synthesized particles have a complex
shape and composition. At the inner surfaces of the HHPC thin-walled
microtubes were found. An attempt is made to explain
the observed anomalies basing on fission
reactions of intermediate mass (downstream reactions) and reactions of fusion
of elements from hydrogen and heavier nuclei (upstream reactions).
|
E9-2014-8 (804.616)
Smirnov V.L., Vorozhtsov S.B., Vincent J.
H- Superconducting Cyclotron for PET Isotope Production
The scientific design of a 14-MeV H- compact superconducting cyclotron
for producing of the 18F and 13N isotopes has been developed. Main
requirements to the facility as a medical accelerator are met in the design.
In particular, the main requirement for the cyclotron was the smallest
possible size due to the superconducting magnet. The calculations show that
the proposed cyclotron allows extracted beam intensity over 500  A. To
increase system reliability and production rates, an external H- ion
source is applied. The choice of the cyclotron concept, design of the
structure elements, calculation of the electromagnetic fields and beam
dynamics from the ion source to the extraction system were performed. A. To
increase system reliability and production rates, an external H- ion
source is applied. The choice of the cyclotron concept, design of the
structure elements, calculation of the electromagnetic fields and beam
dynamics from the ion source to the extraction system were performed.
|
E18-2014-11 (445.640)
Nekhoroshkov P.S. et al.
Neutron Activation Analysis and Scanning Electron Microscopy
of Phytoplankton in the Coastal Zone of the Ñrimea (Black Sea)
For the first time the concentrations of 45 elements in the coastal phytoplankton
communities used as bioindicator of inorganic contamination of the Black Sea coastal area near Sevastopol,
Ukraine, were determined by means of neutron activation analysis and scanning electron microscopy with
energy dispersive spectrometer. Phytoplankton samples were collected by total tows of the plankton net
with 35  m pore size at 3 stations situated in polluted and relatively
pristine water areas of the
Sevastopol coastal zone during autumn period of the phytoplankton active growth. The concentration of
Mg, Al, Sc, Ti, V, Mn, As, Rb, Ba, Th and Fe, Cr increases exponentially from relatively pristine station
to more polluted station and 10 and 3 times greater, respectively, in the phytoplankton of the Sevastopol
Bay. The rare-earth elements have relatively the same concentration values of about
1 m pore size at 3 stations situated in polluted and relatively
pristine water areas of the
Sevastopol coastal zone during autumn period of the phytoplankton active growth. The concentration of
Mg, Al, Sc, Ti, V, Mn, As, Rb, Ba, Th and Fe, Cr increases exponentially from relatively pristine station
to more polluted station and 10 and 3 times greater, respectively, in the phytoplankton of the Sevastopol
Bay. The rare-earth elements have relatively the same concentration values of about
1  g/g and tend
to accumulate in the phytoplankton from the polluted station in the Sevastopol Bay. The obtained results
are in good agreement with the elemental concentration data in the oceanic plankton, plankton communities
from the White Sea and the Black Sea. Using energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometry the mineral particles of
unknown origin and impurities of copper
(0.42% by weight) in the phytoplankton at the polluted station and zinc
(0.57% by weight) at the relatively pristine station were determined. g/g and tend
to accumulate in the phytoplankton from the polluted station in the Sevastopol Bay. The obtained results
are in good agreement with the elemental concentration data in the oceanic plankton, plankton communities
from the White Sea and the Black Sea. Using energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometry the mineral particles of
unknown origin and impurities of copper
(0.42% by weight) in the phytoplankton at the polluted station and zinc
(0.57% by weight) at the relatively pristine station were determined.
|
P13-2014-14 (329.619)
Pepelyshev Yu.N., Popov A.K., Sumkhuu D.
Model Dynamics of the IBR-2M Pulsed Reactor for Study of Transient Processes
in a Wide Range Change of Power
The variant is the model dynamics of the IBR-2M pulsed reactor for
modeling of a wide range at changes of reactivity and power. Consider
nonlinearities of control rods and transfer coefficients of energy and
amplitude of pulse power. Acceptability of the model is confirmed by
comparing the modeled processes with registered at reset emergency
protection when the controlled parameter (relative amplitude of the pulse
power) decreases almost by five orders. Modeling is carried out at different
levels of mean power (0.2-2 MW). With a decrease in the relative amplitude
of the power pulse approximately by the first four orders a good approximation of the
modeled processes is registered. At further decreasing of the amplitude a
certain
difference is observed. However, at such low power levels, this difference is
insignificant.
|
E1-2014-18 (714.370)
Budagov J. et al. (on behalf of the CDF Collaboration)
Top-Quark Mass Measurement in the 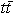 -Dilepton Channel
Using the Full CDF Run II Data Set -Dilepton Channel
Using the Full CDF Run II Data Set
We present a measurement of the top-quark mass with 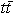 -dilepton events using
the full CDF Run II data set,
which corresponds to an integrated luminosity of 9.1 fb-1 collected from -dilepton events using
the full CDF Run II data set,
which corresponds to an integrated luminosity of 9.1 fb-1 collected from
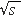 = 1.96 TeV = 1.96 TeV 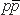 collisions at the Fermilab Tevatron.
A sample of 520 events is obtained after all selection requirements.
The top-quark mass is estimated by a fit of the distribution of some variable to a sum of signal and background contributions.
This variable is defined using special approach to reduce the systematic error due to the jet energy scale uncertainty.
Templates are built from simulated
collisions at the Fermilab Tevatron.
A sample of 520 events is obtained after all selection requirements.
The top-quark mass is estimated by a fit of the distribution of some variable to a sum of signal and background contributions.
This variable is defined using special approach to reduce the systematic error due to the jet energy scale uncertainty.
Templates are built from simulated 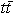 and background events, and parameterized in order to provide probability
distribution functions.
A likelihood fit of the data returns the top-quark mass of
(170.80 and background events, and parameterized in order to provide probability
distribution functions.
A likelihood fit of the data returns the top-quark mass of
(170.80 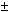 1.83 (stat.) 1.83 (stat.) 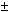 2.69 (syst.)) GeV/c2
(or (170.80 2.69 (syst.)) GeV/c2
(or (170.80 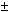 3.25) GeV/c2). 3.25) GeV/c2).
|
P11-2014-19 (319.299)
Lakhno V.D. et al.
Polaron Model of the Hydrated Electron States Formation
Formation of the photoexcited electron states in water is numerically
analysed in the framework of the dynamic polaron model. Results of numerical
simulation are discussed in comparison with experimental data and
theoretical estimations.
|
P13-2014-20 (646.268)
Kononenko G.A. et al
Detection System of the COMBAS Fragment Separator
The results of design and testing of multi-detector telescope
(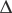 E1, E1, 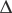 E2, E) are given. The compact telescope consists of
32-strip Si E2, E) are given. The compact telescope consists of
32-strip Si 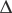 E-detectors and CsI/Tl E-scintillation detectors of
high granularity (nine modules) and allows one to obtain timing signal from Si
detectors for TOF measurements. The single channel and 32-channel
charge-sensitive preamplifiers were developed and manufactured to serve the
Si E-detectors and CsI/Tl E-scintillation detectors of
high granularity (nine modules) and allows one to obtain timing signal from Si
detectors for TOF measurements. The single channel and 32-channel
charge-sensitive preamplifiers were developed and manufactured to serve the
Si 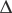 E-detectors and CsI/Tl scintillation E-detectors with high
efficiency and sensitivity. Unambiguous A and Z identification of
reaction products, produced in the 40Ar (35 MeV/nucleon) + 9Âå
reaction system, is implemented. E-detectors and CsI/Tl scintillation E-detectors with high
efficiency and sensitivity. Unambiguous A and Z identification of
reaction products, produced in the 40Ar (35 MeV/nucleon) + 9Âå
reaction system, is implemented.
|
E13-2014-21 (2.406.944)
Batusov V. et al.
Recent Advances and Perspectives of the High Precision Laser Metrology
The laser-based metrology presents new means and opens possibilities
in solving tasks where achievement of a high precision survey is of the
principal significance necessity.
The extended laser fiducial line (coordinate axis) is necessary for
precision alignment of basic structure units of large-scale accelerators,
for precision assembly of subdetectors when mounting large spectrometric
complexes, for online control of space stability of particle detectors
during the data taking period.
The high sensitivity laser inclinometers open the new possibilities for
ground motion control and for accelerator (collider) beam space stabilization
essential for achievement of stable high intensity (luminosity) at the
interaction area.
|
P13-2014-22 (209.207)
Drozdziel A. et al.
Spectrometer for Studying Thermal Desorption of Ar+ Ions from Silicon Samples
The paper describes the design of the thermal desorption spectrometer. The
primary results of the study of thermal desorption phenomena using this
facility are also given. The object of the research was the Ar+
implanted silicon samples. Implantation energy Ei varied in the range
85-175 keV. The measurements were carried out at an annealing temperature of
~ 930 Ê and implantation fluence of 5  1016 cm-2.
Analyzing the TDS spectra collected for different heating ramp rates enabled
estimation of the desorption activation energy (2 eV for Ei = 85 keV and
1.7 eV for Ei = 115 keV). 1016 cm-2.
Analyzing the TDS spectra collected for different heating ramp rates enabled
estimation of the desorption activation energy (2 eV for Ei = 85 keV and
1.7 eV for Ei = 115 keV).
|
P13-2014-23 (201.746)
Hrub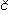 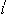 n L. et al. n L. et al.
Characteristics of Silicon Carbide Detectors
The main characteristics of the detectors fabricated on the basis of
high-purity epitaxial layers of 4H-SiC-polytype are presented. It is shown
that the SiC-detectors have good spectrometric characteristics at 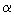 -particle and X-ray registration. -particle and X-ray registration.
|
P13-2014-25 (720.114)
Butler A. et al.
Measurement of the Energy Resolution and Calibration
of Hybrid Pixel Detectors with GaAs:Cr Sensor and Timepix Readout Chip
This paper describes an iterative method of per-pixel energy calibration of
hybrid pixel detectors with GaAs:Cr sensor and Timepix readout chip. A
convolution of precisely measured spectra of characteristic X-rays of
different metals with the resolution and the efficiency of the pixel
detector is used for the calibration. The energy resolution of the detector
is also measured during the calibration. The use of per-pixel calibration
allows one to achieve a good energy resolution of the Timepix detector with
GaAs:Cr sensor: ~ 8% and ~ 13% at 60 keV and 20 keV, respectively.
|
P17-2014-30 (1.961.495)
Rahmonov I.R., Shukrinov Yu.M., Irie A.
Parametric Resonance in the System of Long Josephson Junctions
Based on the investigations of phase dynamics of long Josephson junction system with length
larger than the Josephson penetration depth, we show the possibility of appearance of longitudinal plasma wave
and realization of parametric resonance. Calculations are performed taking into account both inductive and
capacitive coupling between the Josephson junctions. Current-voltage characteristics, spatiotemporal dependence
of electrical charge in the superconducting layers and magnetic field in all the Josephson junctions of the
system have been calculated. In the parametric resonance region starting from a certain length of Josephson
junctions we observe the coexistence of longitudinal plasma waves and fluxon states.
|
P13-2014-31 (781.006)
Ananiev V.D. et al.
Physical Start-Up of the IBR-2M Reactor. Core Fuel Loading
The results of the work on core fuel loading and bringing the IBR-2M
reactor to critical state,
carried out by the JINR FLNP researchers in accordance
with the Program of physical start-up of the modernized IBR-2 reactor,
are presented. Core fuel loading of IBR-2M was begun on 17 December 2010 and
completed on 14 February 2011.
|
P13-2014-33 (530.304)
Ignatovich V.K. et al.
Automation of Experiments in the Field of Neutron Spectrometry
Using Network Technologies
Standardized means of description of experimental procedures and of control
of the operations sequence, which do not require editing experiment control
system components, when experimental procedure is changed, are proposed.
|
P3-2014-34 (165.427)
Êiselev Ì.À. et al.
Investigation of Structure of the Unilamellar DMPC Vesicles in the
Sucrose Solutions by the Small Angle Neutron and X-ray Scattering
The structure of polydispersed population of the unilamellar DMPC vesicles in
sucrose solutions has been investigated by the small angle neutron
scattering (SANS) and X-ray scattering (SAXS). Calculations in frames of the
separated form factors model (SFF) show that the structure of the vesicle
system essentially depends on the sucrose concentration.
|
E2-2014-35 (599.892)
Tokarev M.V., Zborovsk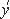 I., Aparin A.A. I., Aparin A.A.
Fractal Structure of Hadrons in Processes with Polarized Protons at SPD NICA
(Proposal for Experiment)
The concept of z-scaling previously developed for analysis of inclusive
reactions in proton-proton collisions is applied for description of
processes with polarized protons at the planned Spin Physics Detector NICA
in Dubna. A hypothesis of self-similarity and fractality of the proton spin
structure is discussed. The possibilities to extract information on
spin-dependent fractal dimensions of hadrons and fragmentation process from
asymmetries and coefficients of polarization transfer are justified. The
double longitudinal spin asymmetry ALL of 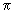 0-meson
production and the coefficient of the polarization transfer DLL of 0-meson
production and the coefficient of the polarization transfer DLL of
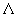 hyperon production in proton-proton collisions measured at RHIC
are analyzed in the framework of z-scaling. The spin-dependent fractal
dimensions of proton and fragmentation process with polarized hyperon production in proton-proton collisions measured at RHIC
are analyzed in the framework of z-scaling. The spin-dependent fractal
dimensions of proton and fragmentation process with polarized 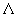 hyperon are estimated.
A study of the spin-dependent constituent energy loss
as a function of transverse momentum of the inclusive hadron and collision
energy is suggested. hyperon are estimated.
A study of the spin-dependent constituent energy loss
as a function of transverse momentum of the inclusive hadron and collision
energy is suggested.
|
P13-2014-36 (1.059.954)
Pepelyshev Yu.N., Tsogtsaikhan Ts.
Cluster Analysis for Investigation of the Dynamics of Pulse Energy Noise at
the IBR-2M Reactor
The results of study of the dynamics of the noise component of IBR-2M using
cluster analysis methods are presented. It is shown that spectral density
changes of pulse energy fluctuations after the reactor nominal power 2 MW
have a transition region of duration ~ 3 days. During the operation of
the reactor the noise structure is divided into four stable structures,
three of them describing the noise transition region. The fourth stable
structure is independent of the reactor's noise level and operation time.
The noise transition region is caused by the vibration of moving reflectors
in the process of heating after increasing of the reactor power.
|
E13-2014-37 (465.546)
Pavlov S.S. et al.
Automation System for Measurement of Gamma-Ray Spectra
of Induced Activity for Multi-Element High-Volume Neutron Activation Analysis
at the IBR-2 Reactor of FLNP at JINR
The automation system for measurement of induced activity of gamma-ray spectra
for multi-element high-volume neutron activation analysis (NAA) was designed, developed and implemented
at the IBR-2 reactor. The system consists of three devices of automatic sample changers for three
Canberra HPGe detector-based gamma spectrometry systems. Each sample changer consists of two-axis
linear positioning module M202A by DriveSet (DriveSet.de) company and disk with 45 slots for containers
with samples. Control of automatic sample changer is performed by the Xemo S360U controller by Systec
(systec.de) company. Positioning accuracy can reach 0.1 mm. Special software performs automatic changing
of samples and measurement of gamma spectra at constant interaction with the NAA database. The system
is unique and can be recommended for other laboratories as one of the possible ways of the NAA integrated automation.
|
P15-2014-38 (844.833)
Didyk A.Yu., Wi niewski R. niewski R.
Properties of Carbon-Based Structures Synthesized in Nuclear
Reactions under Braking  -Quanta Irradiation with 10 MeV Threshold
Energy at 1.1 kbar Helium Gas Pressure -Quanta Irradiation with 10 MeV Threshold
Energy at 1.1 kbar Helium Gas Pressure
The helium gas at 1.1 kbar initial pressure inside a helium high-pressure chamber (HeHPC)
was irradiated by braking  -quanta with 10 MeV
threshold energy during 1.0 -quanta with 10 MeV
threshold energy during 1.0  105 s at the electron beam current
22-24 105 s at the electron beam current
22-24  A.
The helium gas
pressure before opening of the HeHPC was found to be 426 bar. The synthesized black foils and other objects were observed
inside the HeHPC and on the inner surfaces of the reactive chamber
consisting of high purity copper (99.99), a beryllium bronze entrance
window and a copper collector of chemical and nuclear reaction products.
Elemental analysis using scanning electronic microscopy (SEM) and microprobe
roentgen analysis (MPRA) allowed one to establish that the observed foils consist predominantly of carbon and with
smaller quantities of other elements from carbon to iron. The explanation of the observed phenomena and anomalies is
given on the basis of helium fusion nuclear reactions by analogy with nuclear
reactions taking place in stars. The developed approach agrees well with the
series of studies carried out by authors at A.
The helium gas
pressure before opening of the HeHPC was found to be 426 bar. The synthesized black foils and other objects were observed
inside the HeHPC and on the inner surfaces of the reactive chamber
consisting of high purity copper (99.99), a beryllium bronze entrance
window and a copper collector of chemical and nuclear reaction products.
Elemental analysis using scanning electronic microscopy (SEM) and microprobe
roentgen analysis (MPRA) allowed one to establish that the observed foils consist predominantly of carbon and with
smaller quantities of other elements from carbon to iron. The explanation of the observed phenomena and anomalies is
given on the basis of helium fusion nuclear reactions by analogy with nuclear
reactions taking place in stars. The developed approach agrees well with the
series of studies carried out by authors at  -quanta influence on
dense hydrogen and deuterium gases with or without presence of metals in the
reactive chamber. -quanta influence on
dense hydrogen and deuterium gases with or without presence of metals in the
reactive chamber.
|
E19-2014-39 (703.666)
Belov O.V. et al.
A Quantitative Model of the Major Pathways for Radiation-Induced DNA
Double-Strand Break Repair
We have developed a model approach to simulate the major pathways of DNA
double-strand break (DSB) repair in mammalian and human cells. The proposed
model shows a possible mechanistic explanation of the basic regularities of
DSB processing through the nonhomologous end-joining (NHEJ), homologous
recombination (HR), and single-strand annealing (SSA). It reconstructs the
time-courses of radiation-induced foci specific to particular repair
processes including the major intermediate stages. The model is validated
for ionizing radiations of a wide range of linear energy transfer (0.2-236
keV/ m) including a relatively broad spectrum of heavy ions. The
appropriate set of reaction rate constants was suggested to satisfy the
kinetics of DSB rejoining for the considered types of exposure. The
simultaneous assessment of three repair pathways allows one to describe their
possible biological relations in response to radiation. With the help of the
proposed approach, we reproduce several experimental data sets on m) including a relatively broad spectrum of heavy ions. The
appropriate set of reaction rate constants was suggested to satisfy the
kinetics of DSB rejoining for the considered types of exposure. The
simultaneous assessment of three repair pathways allows one to describe their
possible biological relations in response to radiation. With the help of the
proposed approach, we reproduce several experimental data sets on
 -H2AX foci remaining in different types of cells including those defective
in NHEJ, HR, or SSA functions. -H2AX foci remaining in different types of cells including those defective
in NHEJ, HR, or SSA functions.
|
P14-2014-41 (303.860)
Savin V.V., Semin V.A., Semina V.K.
Formation and Stability of the E93-Type Phases in Ni-Nb
Alloy System Studied by X-Ray and Neutron Diffraction
By analyzing phase states formed in the
Ni60-30Nb40-70 alloys under rapid melt quenching
conditions and metal glasses crystallization, some researchers have revealed
formation of two isotypic E93-type phases, denoted as 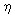 '
and '
and 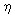 '', which exhibit different lattice parameters:
(1.120 '', which exhibit different lattice parameters:
(1.120 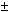 0.001) nm ( 0.001) nm (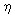 ') and (1.164 ') and (1.164 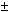 0.002) nm
( 0.002) nm
(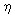 '').
To refine structures of these phases and to clarify
their formation reasons in course of non-equilibrium crystallization of
undercooled melt and amorphous alloy, we used X-ray and neutron diffraction
methods as well as crystallochemical criteria from the theory of formation
and stability for intermediate phases and metal glasses in transition metal
systems. It was experimentally shown that the '').
To refine structures of these phases and to clarify
their formation reasons in course of non-equilibrium crystallization of
undercooled melt and amorphous alloy, we used X-ray and neutron diffraction
methods as well as crystallochemical criteria from the theory of formation
and stability for intermediate phases and metal glasses in transition metal
systems. It was experimentally shown that the 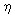 ' and ' and 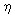 ''
phases belong to different
structural types, namely
Fe6W6C and Ti2Ni, respectively. Formation of these phases is
correlated with respective crystallochemical parameters: the size factor and
electron concentration. ''
phases belong to different
structural types, namely
Fe6W6C and Ti2Ni, respectively. Formation of these phases is
correlated with respective crystallochemical parameters: the size factor and
electron concentration.
|
P13-2014-44 (226.422)
Marachev A.A. et al.
Reactivity Meter of the Pulsed Reactor of Periodic Operation IBR-2M
A reactivity meter of the pulsed reactor of periodic operation of the IBR-2 type is
created. Kinetics of the reactor is described by difference equations
relating the reactor parameters corresponding to the current and preceding
pulse power and the nonlinear dependence of energy of the pulse and its
amplitude on the reactivity. It was taken into consideration that a
controllable parameter of the reactor is the relative deviation of power
pulse amplitude from its base (given mean) value. In the study of transient
processes for suppressing significant reactivity noise inherent in the
design and principle of operation of the reactor, a statistically optimal
filter is used. The best place to include the filter in a block diagram of
the reactivity meter is chosen and the optimal value of the smoothing
coefficient is determined.
|
P5-2014-45 (864.036)
Dikusar N.D.
Polynomial Approximation of the High Orders
The new approach is proposed to the high orders polynomial approximation
(smoothing), based on the basic elements method (BEM).
The nth-degree BEM-polynomial is expressed in
the form of four basic elements, given at a three-point grid
x0 + 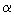 < x0 < x0 + < x0 < x0 + 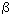 , ,
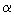 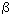 < 0.
Formulae of calculation coefficients of the 12th order polynomial model depending on
length of an interval, continuous parameters < 0.
Formulae of calculation coefficients of the 12th order polynomial model depending on
length of an interval, continuous parameters
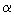 , ,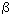 and values of derivatives
f(m)(x0 + and values of derivatives
f(m)(x0 + 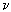 ), ),
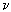 = = 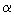 , ,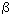 ,0,
m = ,0,
m = 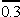 are received. Application of the BEM-polynomial of high degrees for piecewise polynomial approximations (PWA)
and smoothing increases stability and accuracy of calculations at
growth of a step of a grid,
and downturns computing complexity as well.
are received. Application of the BEM-polynomial of high degrees for piecewise polynomial approximations (PWA)
and smoothing increases stability and accuracy of calculations at
growth of a step of a grid,
and downturns computing complexity as well.
|
P3-2014-46 (1.073.026)
Balagurov A.M. et al.
Neutron Scattering for Lithium-Ion Batteries: Analysis of Materials and Processes
The use of neutron scattering to study the structure of materials used in
portable power sources (mainly lithium-ion batteries) and to examine the
structural changes of these materials during the electrochemical processes
is reviewed. We consider the applications of several basic techniques:
diffraction, small angle and inelastic neutron scattering, neutron
reflectometry and neutron imaging. The experimental facilities that already
exist in advanced neutron sources and a series of representative experiments
are reviewed. The results of some studies of lithium-containing materials
and lithium-ion batteries performed at the IBR-2 pulsed research reactor at
the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research (Dubna) are presented.
|
E19-2014-48 (957.645)
Batmunkh M. et al.
Simulation of Energy Deposition from 125I and 213Bi Decays
in the Cell Nucleus
We modeled the radioactive decays of 125I and 213Bi radionuclides
inside the spherical volume simulating a cell nucleus. Using the Monte-Carlo-based track structure
simulation technique, we estimated the radial
distribution of deposited energy and the kinetic energy spectra of electrons
produced by primary particles resulting from decay. To address the
possibility of DNA damage, we performed the cluster analysis of track
structures of emitted particles inside the volumes corresponding to the
diameter of the native double-stranded DNA. For this purpose,
G4-RadioactiveDecay and G4-DNA program packages form the Geant4 Monte Carlo toolkit were combined
together.
|
P15-2014-50 (9.128.840)
Didyk A.Yu., Wi niewski R. niewski R.
Nuclear Reactions, Synthesis of Chemical Elements and Novel Structures
in Dense Helium at 1.1 kbar Pressure under the Action of Braking  -rays with
10 MeV Threshold Energy -rays with
10 MeV Threshold Energy
A helium high pressure chamber (HeHPC) filled with helium gas at 1.1 kbar
initial pressure was irradiated by braking  -rays with 10 MeV threshold energy during
1.0 -rays with 10 MeV threshold energy during
1.0  105 s at the electron beam current 21-24 105 s at the electron beam current 21-24  A.
The helium gas pressure before
opening of the HeHPC was found to be 426 bar. The synthesized black color foils and other objects
were observed inside the HeHPC and on the inner surfaces of the reaction chamber from high purity
copper (99.99%), beryllium bronze entrance window and copper collector of chemical and nuclear
reaction products. An element analysis using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and microprobe
Roentgen analysis (MPRA) permitted us to establish that the observed foils consist predominantly
of carbon with smaller quantities of other elements from carbon to iron. The explanation of the
observed phenomena and anomalies is introduced on the basis of helium fusion nuclear reactions
by analogy with nuclear reactions taking place in stars in astrophysics. The developed approach
agrees well with the series of studies carried out by the authors on the influence of A.
The helium gas pressure before
opening of the HeHPC was found to be 426 bar. The synthesized black color foils and other objects
were observed inside the HeHPC and on the inner surfaces of the reaction chamber from high purity
copper (99.99%), beryllium bronze entrance window and copper collector of chemical and nuclear
reaction products. An element analysis using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and microprobe
Roentgen analysis (MPRA) permitted us to establish that the observed foils consist predominantly
of carbon with smaller quantities of other elements from carbon to iron. The explanation of the
observed phenomena and anomalies is introduced on the basis of helium fusion nuclear reactions
by analogy with nuclear reactions taking place in stars in astrophysics. The developed approach
agrees well with the series of studies carried out by the authors on the influence of  -rays
on dense hydrogen and deuterium gases in the presence or absence of metals in the reaction chamber. -rays
on dense hydrogen and deuterium gases in the presence or absence of metals in the reaction chamber.
|
P10-2014-53 (356.330)
Morkovnikow I.A.
Configuration Files Processing in Sonix+
The work is dedicated to configuration files processing in software package
Sonix+. The work contains a list of software data processing drawbacks and
their solutions. The structure of configuration files was formalized and the
model providing editing of configurations files was developed during the
work. The document contains logic of functions related with data processing
and description of additional functions for developers.
|
E2-2014-54 (104.982)
Beshtoev Kh.M.
Violation of CP Invariance for Neutral K0, D0,
B0d, B0s
Mesons and Quarks in Weak Interactions
CP violation in the Kobayashi-Maskawa matrix was introduced by using phase
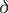 which is the same for the three families of quarks. However, analysis of CP violation
of mesons has shown that new small-angle mixings appear besides of CP phases. This work is devoted
to the consideration of possible schemes for introducing CP violation. It is noted that in general
case it is not correct to use CP phase only for the first and third quark families as it is usually
introduced. CP phase has to be presented for all quark families, and moreover these phases cannot be
the same for all families. Besides, a common case of CP violation was considered for K0,
D0, B0d,
B0s mesons, where mixing angles and phases are present at
CP violation. Expressions
for transition probabilities for these processes are given. In conclusion, mixing of d, s,
b quarks
at CP violation was considered with taking into account their angle mixings and phases. which is the same for the three families of quarks. However, analysis of CP violation
of mesons has shown that new small-angle mixings appear besides of CP phases. This work is devoted
to the consideration of possible schemes for introducing CP violation. It is noted that in general
case it is not correct to use CP phase only for the first and third quark families as it is usually
introduced. CP phase has to be presented for all quark families, and moreover these phases cannot be
the same for all families. Besides, a common case of CP violation was considered for K0,
D0, B0d,
B0s mesons, where mixing angles and phases are present at
CP violation. Expressions
for transition probabilities for these processes are given. In conclusion, mixing of d, s,
b quarks
at CP violation was considered with taking into account their angle mixings and phases.
|
E18-2014-57 (131.546)
Karamian S.A., Dmitriev S.N.
Prospects for the Methods of Radionuclide Production
Methods of radionuclide production for the
nuclear-medicine purposes are described. In a budget approach, the
application of low-energy accelerators is especially advantageous. Intense
flux of bremsstrahlung at electron accelerators or high-current cyclotron
beams of alpha particles must supply a great yield for many isotopes. The
choice of a target material and of the projectile energy provides enough
variation for concrete species formation. The innovating procedures are here
proposed for optimizing of methods, for instance, application of the
noble-gas target for production and transport of activities. The known and
new variants of the «generator» scheme are discussed. Many isotopes are
listed as promising in the context of the therapeutic and theragnostic
applications. Among them are isotopes/isomers emitting soft radiation for
the selective and careful body treatment, also the positron emitters for
PET, and the halogen and alkali-metal species convenient for chemical
separation.
|
P15-2014-58 (227.196)
Karamian S.A. et al.
Production of Isotopes and Isomers with Irradiation of
Z = 47-50 Targets by 23 MeV Bremsstrahlung
The irradiations of Ag to Sn targets by bremsstrahlung generated with 23 MeV
electron beams are performed at the MT-25 microtron. Gamma spectra of the
induced activities have been measured and the yields of all detected
radio-nuclides and isomers are carefully measured and analyzed. A regular
dependence of yields versus changed reaction threshold is confirmed. Many
isomers are detected and the suppression of the production-probability is
observed with growing product spin. Special peculiarities for the
isomer-to-ground state ratios were deduced for the 106mAg, 108mAg,
113mIn, 115mIn, and 123mSn isomers. The production of such
nuclides as 108mAg, 115mIn, 117m,gIn, and 113mCd is of
interest for applications, especially when economic methods are available.
|
P3-2014-59 (127.761)
Aksenov V.L. et al.
Reflectometric Investigations in Connection with Neutron Wave Packet Representation
A preliminary experiment on neutron reflection from a glass plate with wave vectors
lower than the critical one is described.
The data have been analyzed by neutron wave packet representation. The limiting value of neutron transmission
through the glass plate for the neutron wave packet representation is defined as
(3.0 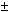 1.0) 1.0)  10-5. 10-5.
|
P14-2014-60 (336.117)
Nikitenko Yu.V. et al.
Detection of Magnetic Nanolattice in Structure
Ta/V/Fe0.7V0.3/V/Fe0.7V0.3/Nb/Si
with Magnetic and Superconducting Layers
Formation of magnetic lattice in structure
Ta/V/Fe0.7V0.3/V/Fe0.7V0.3/Nb/Si with magnetic
and superconducting layers at low temperatures 1.3-10 K is observed.
It definitely points to the realization of the crypto-ferromagnetic state at
the «ferromagnetic-superconductor» interface.
|
P13-2014-61 (538.023)
Pepelyshev Yu.N., Tsogtsaikhan Ts.
The Noise Effects of Liquid Sodium Coolant System of IBR-2M on
Reactivity Fluctuation
In this paper we consider the thermal dynamics vibration parameters of the
primary circuit of the sodium cooling system of IBR-2M reactor at an average
power of 2 MW and sodium flow through the core of 100 m3/h. The data
on the statistics of the contour fluctuations, their relationship and
assessment of the impact of noise on the circuit noise reactivity and power
stabilization system are obtained.
The full variation of parameters of the primary circuit of the sodium
cooling system is sufficiently large, up to 6-8%. In the fluctuation of
the power spectral density of the first circuit parameters, total reactivity
and power feedback reactivity, the frequency of daily fluctuations is
prevalent, with a significant contribution of the weekly noise components.
The automatic regulator (AR) in the reactor feedback loop may undergo a
substantial per night vibrational displacement of 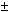 66 mm with
additional weekly movements of 66 mm with
additional weekly movements of 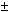 46 mm. Given the trend of reactivity
compensation by the system of automatic power stabilization, full daily
fluctuations of AR reach 100 mm, which completely covers the linear region
of power control. The total reactivity fluctuations for the reactor cycle are
14.0 46 mm. Given the trend of reactivity
compensation by the system of automatic power stabilization, full daily
fluctuations of AR reach 100 mm, which completely covers the linear region
of power control. The total reactivity fluctuations for the reactor cycle are
14.0  10-2 10-2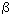 ef and cause movement of AR by 310 mm.
Argon pressure fluctuations in the core (~ 8%) and sodium levels
(4.5 cm) give a zero isobaric effect and do not affect the power
fluctuations.
The slow fluctuation of the parameters of the first coolant circuit in the
core make a sufficiently strong influence on the reactivity, operation of
the power stabilization system, and safety of the reactor. ef and cause movement of AR by 310 mm.
Argon pressure fluctuations in the core (~ 8%) and sodium levels
(4.5 cm) give a zero isobaric effect and do not affect the power
fluctuations.
The slow fluctuation of the parameters of the first coolant circuit in the
core make a sufficiently strong influence on the reactivity, operation of
the power stabilization system, and safety of the reactor.
|
E2-2014-63 (194.729)
Beshtoev Kh.M.
About Absence of Oscillations at CP Violation and Presence of
Interference between KS-, KL-Meson States in the System of
K0 Mesons
Two approaches to the
description of K0-, 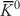 -meson transitions into
K01
mesons at CP violation in weak interactions are considered.
The first approach uses the standard theory of oscillations and the second
approach supposes that (KS, KL) states which arise at CP violation
are normalized but not orthogonal state functions, then there arise
interferences between these states but not oscillations. It is
necessary to remark that the available experimental data are in
good agreement with the second approach. So, we come to the
conclusion that oscillations do not arise at CP violation in
weak interactions in the system of K0 mesons. Only interference
between KS and KL states takes place here. -meson transitions into
K01
mesons at CP violation in weak interactions are considered.
The first approach uses the standard theory of oscillations and the second
approach supposes that (KS, KL) states which arise at CP violation
are normalized but not orthogonal state functions, then there arise
interferences between these states but not oscillations. It is
necessary to remark that the available experimental data are in
good agreement with the second approach. So, we come to the
conclusion that oscillations do not arise at CP violation in
weak interactions in the system of K0 mesons. Only interference
between KS and KL states takes place here.
|
E2-2014-66 (334.388)
Shirkov D.V.
Remarks on Simple Modified Perturbation Theory
The goal is to devise a pQCD modification that should be regular in the
low-energy region and could serve practically for the data analysis
below 1 GeV up to the IR limit.
The recently observed "blow-up" of the 4-loop pQCD series for the Bjorken
SR form factor around Q 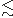 1 GeV and partial resolving of the issue
with the help of the Analytic Perturbation Theory
(APT) until Q ~ 0.6 GeV provided the impetus for this attempt. 1 GeV and partial resolving of the issue
with the help of the Analytic Perturbation Theory
(APT) until Q ~ 0.6 GeV provided the impetus for this attempt.
The "massive pQCD" under construction has two grounds. The first
is pQCD with only one parameter added, an effective "glueball mass"
m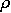 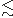 Mglb
Mglb 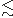 1 GeV, serving as an IR regulator.
Roughly, we introduce it by changing the UV ln Q2 for a massive
log, ln (Q2 + Mglb), regular in the LE region and finite in
the IR limit. The second stems from the ghost-free APT comprising non-power
perturbative expansion that makes it compatible with linear integral
transformations. 1 GeV, serving as an IR regulator.
Roughly, we introduce it by changing the UV ln Q2 for a massive
log, ln (Q2 + Mglb), regular in the LE region and finite in
the IR limit. The second stems from the ghost-free APT comprising non-power
perturbative expansion that makes it compatible with linear integral
transformations.
|
E13-2014-68 (572.898)
Volkov A.D.
Measurement of Tube Tension in Straw Detectors
A device and a method for controlling tension of tubes in straw detectors
are presented. The method is based on measuring the resonance frequency of a tube at electrostatic
excitation of its oscillations relative to the reference electrode. The sensitivity of the device allows
the resonance frequency to be detected with an accuracy of 0.1 Hz. The tension is determined using analytical
dependence obtained by the author. The relative error of the experimental data against the analytical dependence
is below 3%. The device proved to be effective in a range of tensions from 250 to 1200 g/m used in development
of the detectors, and it can be employed for measuring tension of wires.
|
E2-2014-70 (160.115)
Namsrai Kh.
Nonlocal Quantum Electrodynamics
It is shown that an origin of the divergence problem in quantum electrodynamics is associated
with a singularity of classical electrostatic field. A modification of its Coulomb potential at small distances
leads to the change of the photon propagator which allows us to construct finite and gauge-invariant quantum
electrodynamics. We establish restriction on the value of the so-called fundamental length
l 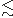 1016 cm
from the experimental data on the measuring anomalous magnetic moment of leptons. It is well known that any
modification of the spinor propagator (in particular, electron one) gives rise to many problems connected with
verification of basic principles of the theory like gauge invariance, unitarity, causality condition and so on.
However, it turns out that square-root modification of the spinor propagator is free from these difficult problems.
Here we also construct a finite square-root quantum electrodynamics. 1016 cm
from the experimental data on the measuring anomalous magnetic moment of leptons. It is well known that any
modification of the spinor propagator (in particular, electron one) gives rise to many problems connected with
verification of basic principles of the theory like gauge invariance, unitarity, causality condition and so on.
However, it turns out that square-root modification of the spinor propagator is free from these difficult problems.
Here we also construct a finite square-root quantum electrodynamics.
|
P3-2014-72 (377.820)
Kulin G.V. et al.
Time-of-Flight Fourier Spectrometry of UCN
The results of preliminary experiments on TOF Fourier UCN spectrometry are
presented. The description of the new Fourier spectrometer that may be used
for the measurement of the UCN spectra arising from diffraction by a moving
grating is given. The results of preliminary experiments and Monte Carlo
calculations give reason to hope for the success of the planned experiment.
|
E2-2014-73 (375.482)
Tokarev M.V., Zborovsk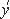 I., Aparin A.A. I., Aparin A.A.
Self-Similarity of Hard Cumulative Processes in Fixed Target
Experiment for BES-II at STAR
Search for signatures of phase transition in Au + Au collisions is in the heart
of the heavy ion program at RHIC. Systematic study of particle
production over a wide range of collision energy revealed new phenomena such
as the nuclear suppression effect expressed by nuclear modification factor,
the constituent quark number scaling for elliptic flow, the "ridge effect"
in
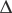 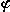 - - 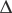 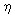 fluctuations, etc. To determine the phase
boundaries and location of the critical point of nuclear matter, the Beam
Energy Scan (BES-I) program at RHIC has been suggested and performed by STAR
and PHENIX Collaborations. The obtained results have shown that the program
(BES-II) should be continued. In this paper a proposal to use hard
cumulative processes in BES Phase-II program is outlined. Selection of the
cumulative events is assumed to enrich data sample by a new type of collisions
characterized by higher energy density and more compressed matter. This
would allow finding clearer signatures of phase transition, location of a
critical point and studying extreme conditions in heavy ion collisions.
fluctuations, etc. To determine the phase
boundaries and location of the critical point of nuclear matter, the Beam
Energy Scan (BES-I) program at RHIC has been suggested and performed by STAR
and PHENIX Collaborations. The obtained results have shown that the program
(BES-II) should be continued. In this paper a proposal to use hard
cumulative processes in BES Phase-II program is outlined. Selection of the
cumulative events is assumed to enrich data sample by a new type of collisions
characterized by higher energy density and more compressed matter. This
would allow finding clearer signatures of phase transition, location of a
critical point and studying extreme conditions in heavy ion collisions.
|
P19-2014-76 (170.814)
Komochkov M.M.
Low Dose Dependence of the Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation
in Different Representations
The essence of the biological effects of low doses of ionizing radiation is
still unclear, which determines the decree character of the linear no-threshold
model underlying the ICRP recommendations. In our opinion, one of the main
causes of this ambiguity is the absence of necessary and sufficient
information on the radiosensitivity of the main elements of biological
objects. Different models fit results of experiments and observations with a
different degree of reliability and themselves evaluate radiosensitivity
based on the best agreement between the calculated and measured data. The
best fitting results are produced by the model of two protective reactions.
|
P3-2014-77 (81.636)
Vasiliev B.V.
Is the Neutron an Elementary Particle?
The question is whether or not the neutron an elementary particle was considered
in the first years after its discovery. There was not any experimental
data which could help to solve this problem at the time. At the moment it
is assumed that the neutron is an elementary particle and that it is
composed of quarks. However, this approach does not allow one to calculate the
specific properties of the neutron. The current experimental information on the properties of the neutron
indicates that it is not an elementary particle.
If we assume that the neutron is a composite particle, then we can calculate the magnetic moment of the neutron
and the energy of its decay.
|
E2-2014-78 (282.502)
Tokarev M.V., Zborovsk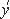 I. I.
Self-Similarity of Proton Spin and Asymmetry of Jet Production
Self-similarity of jet production in polarized p + p collisions is studied.
The concept of z-scaling is applied for description of inclusive spectra
obtained with different orientations of proton spin. New data on the double
longitudinal spin asymmetry, ALL, of jets produced in proton-proton
collisions at 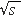 = 200 GeV measured by the STAR Collaboration at
RHIC are analyzed in the z-scaling approach. Hypotheses of
self-similarity and fractality of internal spin structure are formulated. A possibility to extract information
on spin-dependent fractal dimensions of
proton from the asymmetry of jet production is justified. The spin-dependent
fractal dimensions for the process = 200 GeV measured by the STAR Collaboration at
RHIC are analyzed in the z-scaling approach. Hypotheses of
self-similarity and fractality of internal spin structure are formulated. A possibility to extract information
on spin-dependent fractal dimensions of
proton from the asymmetry of jet production is justified. The spin-dependent
fractal dimensions for the process 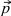 + + 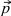 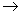 jet + X are
estimated. jet + X are
estimated.
|
E14-2014-80 (400.990)
Uyanga E. et al.
The Structural Study of Alternative Support Materials for PEMFC
Mesoporous niobium-doped titanium oxide (NTO) was synthesized and
investigated as a cathode catalyst support material for polymer electrolyte
membrane fuel cells (PEMFC). We prepared the NTO support by two different
methods: 1) room-temperature synthesis of NbxTi1-xO2
(x = 0.1, 0.005) via surfactant templating and 2) high-temperature synthesis
(700 and 1000 °C) of NbxTi1—xO2 (x = 0.1). The XRD analysis revealed only the presence of anatase and rutile
TiO2 phase in the synthesized support powder. The existence of any peaks belonging to Nb compounds was not observed, indicating that Nb is incorporated in the
lattice. The X-ray diffraction and Raman scattering measurements revealed
anatase-to-rutile phase transition hindering due to Nb doping. Pt
nanoparticles were dispersed in the mesoporous NTO support by the polyol
method and characterized by the scanning electron microscopy. The Pt
particle sizes, interatomic distances, and distribution were found by XRD,
XAS, and SEM. To better understand the role played by the dopant
atoms in inhibiting both phase transformation to rutile and grain growth,
XAS measurements were performed at the Nb K and Ti K absorption edges. The
XAS analysis results indicate that niobium atoms are incorporated into
nanostructured TiO2 with +5 valence state.
|
E15-2014-85 (526.459)
Testov D. et al.
The 3He Long-Counter TETRA at the ALTO ISOL Facility
A new 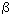 -decay station (BEDO) has been installed after the PARRNe
mass-separator operated online to the electron-driven ALTO ISOL facility. The station is equipped with
a movable tape collector allowing the creation of the radioactive sources of interest at the very center
of a modular detection system and their cyclical evacuation outside of it. The mechanical structure was
designed to host various assemblies of detectors in compact geometry. We report here the first online use
of this system equipped by the 3He neutron counter TETRA built at JINR, Dubna, associated with the HPGe
and plastic 4 -decay station (BEDO) has been installed after the PARRNe
mass-separator operated online to the electron-driven ALTO ISOL facility. The station is equipped with
a movable tape collector allowing the creation of the radioactive sources of interest at the very center
of a modular detection system and their cyclical evacuation outside of it. The mechanical structure was
designed to host various assemblies of detectors in compact geometry. We report here the first online use
of this system equipped by the 3He neutron counter TETRA built at JINR, Dubna, associated with the HPGe
and plastic 4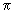 -beta detectors. The single neutron detection efficiency achieved is
(53 -beta detectors. The single neutron detection efficiency achieved is
(53 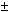 2)% measured
using 252Cf source. The online commissioning of the TETRA was performed with a laser-ionized Ga beams. 2)% measured
using 252Cf source. The online commissioning of the TETRA was performed with a laser-ionized Ga beams.
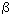 and neutron events were recorded as a function of time. From this data we report
Pn(82Ga) = (22.2 and neutron events were recorded as a function of time. From this data we report
Pn(82Ga) = (22.2 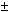 2)% and
T1/2(82Ga) = 0.604(11) s in good agreement
with values available in the literature. We also report
Pn(83Ga) = (84.8 2)% and
T1/2(82Ga) = 0.604(11) s in good agreement
with values available in the literature. We also report
Pn(83Ga) = (84.8 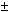 3.6)% measured
by simultaneous 3.6)% measured
by simultaneous 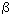 , neutron counting, which confirms that
83Ga is much stronger neutron emitter
than considered before. , neutron counting, which confirms that
83Ga is much stronger neutron emitter
than considered before.
|
P15-2014-87 (1.051.858)
Didyk A.Yu., Wi niewski R. niewski R.
Synthesis of New Structures and Formation of Chemical Elements
in Dense Helium at a Pressure of 3.05 kbar under Irradiation of Braking  -Rays
with a Threshold Energy of 10 MeV -Rays
with a Threshold Energy of 10 MeV
The high-pressure helium chamber (HeHPC) filled with helium gas under a
pressure of about 3.05 kbar was irradiated by braking  -rays of 10 MeV threshold energy
for 1.0 -rays of 10 MeV threshold energy
for 1.0  105 s at an electron beam current of 18-21 105 s at an electron beam current of 18-21  A.
During the irradiation of the HeHPC, the pressure decreased by 65 bar.
Inside the chamber, multiple objects were found at the internal surfaces of
the reaction chamber, input window from beryllium bronze and copper
collector of nuclear and chemical reaction products. The element analysis
made by using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and X-ray microprobe
analysis (XMPA) revealed that the objects mainly consist of carbon and
smaller amounts of other elements from carbon to iron. An explanation of the
observed elements and anomalies based on nuclear fusion reactions of helium
under the action of A.
During the irradiation of the HeHPC, the pressure decreased by 65 bar.
Inside the chamber, multiple objects were found at the internal surfaces of
the reaction chamber, input window from beryllium bronze and copper
collector of nuclear and chemical reaction products. The element analysis
made by using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and X-ray microprobe
analysis (XMPA) revealed that the objects mainly consist of carbon and
smaller amounts of other elements from carbon to iron. An explanation of the
observed elements and anomalies based on nuclear fusion reactions of helium
under the action of  -rays is proposed by analogy with the reactions
taking place in stars in astrophysics. -rays is proposed by analogy with the reactions
taking place in stars in astrophysics.
|
P15-2014-88 (4.069.756)
Didyk A.Yu., Wi niewski R. niewski R.
Nuclear Reactions with Synthesis of Structures in HHPC with Hydrogen
at a Pressure of 3.5 kbar and a Tin Rod under Irradiation of Braking  -Rays with a Threshold Energy of 10 MeV -Rays with a Threshold Energy of 10 MeV
The high-pressure chamber (HHPC) filled with hydrogen under a pressure of
about 3.5~kbar was irradiated by braking  -rays of 10~MeV threshold
energy. Upon opening the HHPC, a large number of synthesized microparticles
detached from the reaction chamber walls and spilled out. Detailed studies
of the element composition and structure of all microobjects detected at
the internal surfaces of the HHPC components and tin rod were conducted. As a result of
irradiation of the HHPC by braking -rays of 10~MeV threshold
energy. Upon opening the HHPC, a large number of synthesized microparticles
detached from the reaction chamber walls and spilled out. Detailed studies
of the element composition and structure of all microobjects detected at
the internal surfaces of the HHPC components and tin rod were conducted. As a result of
irradiation of the HHPC by braking  -rays, nuclear reactions took place with the formation of the light
elements from carbon to medium-mass metals, as well as heavier ones, such as
barium. Possible upward (with synthesis of elements from lighter ones) and
downstream (with fission of heavier nuclei into lighter elements) nuclear
reactions are discussed. -rays, nuclear reactions took place with the formation of the light
elements from carbon to medium-mass metals, as well as heavier ones, such as
barium. Possible upward (with synthesis of elements from lighter ones) and
downstream (with fission of heavier nuclei into lighter elements) nuclear
reactions are discussed.
|
P15-2014-89 (487.678)
Didyk A.Yu., Wi niewski R. niewski R.
Nuclear Reactions with Synthesis of Microparticles in Hydrogen
at a Pressure of 3.5 kbar in the Presence of Tin under Irradiation
by Braking  -Quanta with a Threshold Energy of 10 MeV -Quanta with a Threshold Energy of 10 MeV
A rod of pure (99.98%) tin that was placed in a hydrogen high-pressure chamber
(HHPC) at a pressure of 3.5 kbar was irradiated with braking  -rays
of 10 MeV threshold energy. Upon opening the HHPC, a large number of
synthesized microparticles were detached from the reaction chamber walls and
spilled out. Detailed studies of the element composition and structure of
microparticles and all the internal surfaces of the HHPC components,
including the tin rod, have been carried out. It is found that the
microparticles can be divided into three parts: banded, loose and compact.
As a result of nuclear reactions under the irradiation by braking -rays
of 10 MeV threshold energy. Upon opening the HHPC, a large number of
synthesized microparticles were detached from the reaction chamber walls and
spilled out. Detailed studies of the element composition and structure of
microparticles and all the internal surfaces of the HHPC components,
including the tin rod, have been carried out. It is found that the
microparticles can be divided into three parts: banded, loose and compact.
As a result of nuclear reactions under the irradiation by braking
 -rays, nuclear reactions took place with the formation of light
elements from carbon to medium-mass metals, as well as heavier ones, such as
barium. Possible upward (with synthesis of elements from lighter ones) and
downstream (with fission of heavier nuclei into lighter elements) nuclear
reactions are discussed. -rays, nuclear reactions took place with the formation of light
elements from carbon to medium-mass metals, as well as heavier ones, such as
barium. Possible upward (with synthesis of elements from lighter ones) and
downstream (with fission of heavier nuclei into lighter elements) nuclear
reactions are discussed.
|
P19-2014-91 (540.167)
Dushanov E.B., Kholmurodov Kh.T., Koltovaya N.A.
Computer Modeling of Mutant P32T Homo- and Heterodimers of Human
Inosine Triphosphate Pyrophosphatase hITPA
The structure of the dimer enzyme human inosine
triphosphate pyrophosphatase (hITPA) is considered to identify the enzyme
conformation changes causing the inactivation effect of the P32T mutation. A
nanosecond molecular dynamics (MD) analysis is performed; mean square
deviations are calculated of the structures of the wild-type and mutant
homodimers and the heterodimer. A 3 ns modeling shows a greater displacement
of atoms in mutant protomers. During MD modeling, the strongest changes are
observed in the loop between 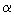 2 and 2 and 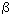 2 (res. 28-33), which
includes P32T, the loop between 2 (res. 28-33), which
includes P32T, the loop between 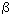 5 and 5 and 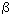 6, and the C-terminal
amino acid residues. The loop between 6, and the C-terminal
amino acid residues. The loop between 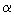 2 and 2 and 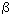 2 has two
conformations characterized by different positions of the Phe31 aromatic
group. The distance between Cys33 (C 2 has two
conformations characterized by different positions of the Phe31 aromatic
group. The distance between Cys33 (C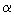 ) and Phe31 (Cz) for
wild-type and mutant protomers was ~ 9 and 5.5 ) and Phe31 (Cz) for
wild-type and mutant protomers was ~ 9 and 5.5 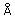 , respectively. These
conformations were stable. , respectively. These
conformations were stable.
|
E3-2014-92 (1.102.868)
Adam J. et al.
Measurement of the High-Energy Neutron Flux on the Surface
of the Natural Uranium Target Assembly QUINTA Irradiated by Deuterons of 4- and 8-GeV Energy
Experiments with a natural uranium target assembly QUINTA exposed to 4- and 8 GeV
deuteron beams of the Nuclotron accelerator at the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research (Dubna) are analyzed.
The 129I, 232Th, 233U, 235U,
natU, 237Np, 238Pu, 239Pu
and 241Am radioactive samples were installed on the surface of the QUINTA set-up and irradiated
with secondary neutrons. The neutron flux through the RA samples was monitored by Al foils.
The reaction rates of
27Al(n,y1)24Na,
27Al(n,y2)22Na and
27Al(n,y2)7Be
reactions with the effective threshold energies of 5, 27 and 119 MeV were measured at both 4-
and 8-GeV deuteron beam energies. The average neutron fluxes between the effective threshold energies
and the effective ends of the neutron spectra (which are 800 or 1000 MeV for energy of 4- or 8-GeV deuterons)
were determined. The evidence for the intensity shift of the neutron spectra to higher neutron energies with
the increase of the deuteron energy from 4 to 8 GeV was found from the ratios of the average neutron fluxes.
The reaction rates and the average neutron fluxes were calculated with MCNPX2.7 and MARS15 codes.
|
E2-2014-93 (141.103)
Pestov I.B.
Symmetry and Quantum Effects of Extra Dimension of Space
It is supposed that the physical space has extra dimension.
Possible effects of this innovation are investigated on the example of the simplest mathematical space -
the four-dimensional Euclidian space. It is demonstrated that the origin and the nature of a rotational
motion are clearly visible in four dimensions only. A pair of the Dirac equations associated with the natural
tetrads on the four-dimensional Euclidian space is considered. Comparing these equations with the original
Dirac equation in the Minkowski space-time, we show that there are two causal structures on the four-dimensional
Euclidian space. With this, the rational proof of the existence of leptons and quarks, lepton-quark symmetry
and confinement is obtained. To illustrate some questions connected with the so-called hidden symmetry and
hidden dimensions, natural mappings of the four-dimensional Euclidian space onto the three-dimensional one
are considered.
|
P3-2014-94 (518.598)
Zlokazov V.B. et al.
Visualization and Analysis of Neutron Diffraction Real-Time Data
For the preliminary analysis and final mathematical processing of large
neutron diffraction data arrays, obtained in studies of transitions
processes in crystals, necessary software has been created. It contains the
program for visualization of 2D data, obtained at a TOF-diffractometer with
time of flight scanning, and the program package, which enables analysis of
the atomic structure changes during the transition process in an automatic
mode. Results of the analysis are temporal dependences of the structural
crystal characteristics of crystal phases, which can be presented as
dependences on outer impact. If needed the package enables the analysis of
data, measured at a constant wavelength diffractometer with scanning along
scattering angle.
|
P1-2014-95 (197.254)
Avramenko S.A. et al.
Fast Search Method for Initial Approximation of Straight Tracks
of the Wire and Strip Detectors
For detectors with sensitive elements in the form of straight line segments, i.e.
for wire detectors, drift tubes, silicon strip detectors, etc., there is a
task to find straight tracks for triggered items (tracking). Due to the large
number of tracks as well as elements of the detectors in modern experiments,
the number of combinations of selected sensitive elements can
be very large.
It turns out that if the number of sensitive elements of the
detector is chosen equal to four, then under some conditions there is a
straight line which strictly crosses all the selected four
elements (four overlapping straight lines).
The proposed "method of four straight lines" can be used, in particular, for
rapid determination of initial approximation and/or selection of items which belong to a
straight track. The method has been successfully used at the facility HADES,
GSI.
|
P4-2014-96 (122.519)
Severyukhin A.P., Sushenok E.O.
Influence of the Complex Configurations on the Description of  -Decay Properties of 132Sn -Decay Properties of 132Sn
We give a microscopic description of Gamow-Teller (GT) transitions in the
case of  -decay of neutron-rich nucleus 132Sn.
Starting from the Skyrme force, the model takes
into account the coupling between one- and two-phonon components of wave
function. The separable approximation allows us to perform the calculations
in very large configuration spaces. It is shown that the increase of the
strength of the neutron-proton tensor interaction leads to the increment of
GT transition energy. Also, there is the reduction of the -decay of neutron-rich nucleus 132Sn.
Starting from the Skyrme force, the model takes
into account the coupling between one- and two-phonon components of wave
function. The separable approximation allows us to perform the calculations
in very large configuration spaces. It is shown that the increase of the
strength of the neutron-proton tensor interaction leads to the increment of
GT transition energy. Also, there is the reduction of the 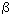 -decay
half-life of 132Sn. -decay
half-life of 132Sn.
|
E13-2014-97 (284.487)
Azaryan N. et al.
The Precision Laser Inclinometer Long-Term Measurement
in Thermo-Stabilized Conditions (First Experimental Data)
The Precision Laser Inclinometer was tested at thermo-stabilized conditions,
and the ground angular stability of 1  rad (observation during 24 h)
and 7 nrad (observation during 60 min) was measured. rad (observation during 24 h)
and 7 nrad (observation during 60 min) was measured.
|
P10-2014-101 (54.836)
Morkovnikov I.A., Kashunin I.A., Sukhomlinov G.A.
Organization of Data Transfer from Sonix+ to the File Server Nfserv-b
The work is dedicated to data storage creation and file transfer automation
from control computer to the file server. The work contains a list of data storage hardware and software,
a description of the file system organization and data security.
|
E10-2014-103 (2.523.051)
Akishina E.P. et al.
Conceptual Considerations for CBM Databases
We consider a concept of databases for the CBM experiment.
For this purpose, an analysis of the databases for large experiments at the LHC at CERN has been performed.
Special features of various DBMS utilized in physical experiments, including relational and object-oriented
DBMS as the most applicable ones for the tasks of these experiments, were analyzed. A set of databases for
the CBM experiment, DBMS for their developments as well as use cases for the considered databases are suggested.
|
P15-2014-104 (421.271)
Didyk A.Yu. et al.
Synthesis of Microparticles in Dense Hydrogen at a Pressure of 3.5 kbar with a Tin Rod under Irradiation with Braking  -Rays of a Threshold Energy of 10~MeV -Rays of a Threshold Energy of 10~MeV
A rod of pure (99.98%) tin was placed in a hydrogen high-pressure chamber (HHPC) at a pressure of 3.5 kbar
was irradiated with braking  -rays of 10 MeV threshold energy. Upon opening the HHPC, a large number of synthesized microparticles detached
from the reaction chamber walls and spilled out. Detailed studies of the element composition and structure of microparticles and all the internal surfaces
of the HHPC components, including the tin rod, have been carried out. It is found that the microparticles can be divided into three types: banded, loose and compact.
As a result of irradiation of the HHPC with the braking -rays of 10 MeV threshold energy. Upon opening the HHPC, a large number of synthesized microparticles detached
from the reaction chamber walls and spilled out. Detailed studies of the element composition and structure of microparticles and all the internal surfaces
of the HHPC components, including the tin rod, have been carried out. It is found that the microparticles can be divided into three types: banded, loose and compact.
As a result of irradiation of the HHPC with the braking  -rays, nuclear reactions took place with the formation of light elements from carbon to medium-mass metals,
as well as heavier ones, such as barium. Possible upward (with synthesis of elements from lighter ones) and downstream (with fission of heavier nuclei into lighter elements)
nuclear reactions are discussed. -rays, nuclear reactions took place with the formation of light elements from carbon to medium-mass metals,
as well as heavier ones, such as barium. Possible upward (with synthesis of elements from lighter ones) and downstream (with fission of heavier nuclei into lighter elements)
nuclear reactions are discussed.
|
