| 2012 |
|
P10-2012-1 (2.661.239)
Kulakov I.S. et al.
Perfomance Analysis of a Cellular Automaton Algorithm for the Solution of the Track Reconstruction Problem
on a Manycore Server at LIT, JINR
The results of the tests for the tracks reconstruction efficiency,
the speed of the algorithm and its scalability with respect to the number of cores of the server with two
Intel Xeon E5640 CPUs (in total 8 physical or 16 logical cores) are presented and discussed.
|
E2-2012-2 (168.559)
Lyuboshitz V.L., Lyuboshitz V.V.
Lepton Mixing under the Lepton-Charge Nonconservation,
Neutrino Masses and Oscillations and the «Forbidden» Decay 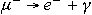
The lepton-charge (Le, L ,
L ,
L ) nonconserving
interaction leads to the mixing of the electron, muon, and tau neutrinos,
which manifests itself in spatial oscillations of a neutrino beam, and also
to the mixing of the electron, negative muon, and ) nonconserving
interaction leads to the mixing of the electron, muon, and tau neutrinos,
which manifests itself in spatial oscillations of a neutrino beam, and also
to the mixing of the electron, negative muon, and  - lepton, which, in
particular, may be the cause of the «forbidden» radiative decay of the
negative muon into the electron and - lepton, which, in
particular, may be the cause of the «forbidden» radiative decay of the
negative muon into the electron and  quantum. Under the assumption
that the nondiagonal elements of the mass matrices for neutrinos and
ordinary leptons, connected with the lepton-charge nonconservation, are the
same, and by performing joint analysis of the experimental data on
neutrino oscillations and experimental restriction for the probability
of the decay quantum. Under the assumption
that the nondiagonal elements of the mass matrices for neutrinos and
ordinary leptons, connected with the lepton-charge nonconservation, are the
same, and by performing joint analysis of the experimental data on
neutrino oscillations and experimental restriction for the probability
of the decay 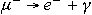 per unit time, the following estimate for
the lower bound of neutrino mass has been obtained: m( per unit time, the following estimate for
the lower bound of neutrino mass has been obtained: m(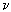 ) > 1.5 eV/c2. ) > 1.5 eV/c2.
|
E14-2012-4 (168.013)
Frontasyeva M.V. et al.
Application of Some Microorganisms for Synthesis of Gold and Silver Nanoparticles
In recent years, much attention has been paid to microbial technologies
of nanoparticle production. Novel strains of actinomycetes Streptomyces glaucus 71MD,
Streptomyces spp. 211A, arthrobacter genera - Arthrobacter globiformis 151B and
Arthrobacter oxydans 61B and blue-green microalga
Spirulina platensis were used for synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles. The studies were
carried out using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive
X-ray analysis (EDAX), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray
diffraction (XRD), atomic absorption spectrometry (AAS), and neutron activation
analysis (NAA).
|
P10-2012-7 (307.777)
Slepov I.P., Ososkov G.A., Rogachevsky O.
Informational Support for Software Development of the MPD Experiment at the NICA Collider
The article presents a web-site which carries information for users and software developers
of the MPD experiment at the NICA collider. It describes usage of the content management system Drupal for
the site creation and tools useful for the software developers of the experiment.
|
E2-2012-8 (100.061)
Beshtoev Kh.M.
About Direct CP Violation in the System of K0 mesons
This work is devoted to computation of the parameter of direct CP violation
by the weak interactions in the system of K0 mesons at
K10-, K20-meson mixings and oscillations
via KS-, KL-meson states.
|
19-2012-10
Зайцева Е. М.
Цитогенетическое действие протонного терапевтического пучка с энергией 170 МЭВ на клетки человека
Автореф. дис. ... канд. биол. наук
(rus)
|
P13-2012-11 (2.971.770)
Kruchonak U. et al.
The Device for Measuring Light Attenuation in the WLS Fibers
The device that allows accurate and fast measurement of optical characteristics
(light output and attenuation length) of wavelength shifting (WLS) fibers is described. This device
was used for test and selection of fibers for the Target Tracker detector of OPERA experiment. After
modification the device was used for the studying and selection of WLS fibers for the electromagnetic
calorimeter ECAL0 of the COMPASS detector.
|
E2-2012-12 (265.731)
Tokarev M.V., Zborovsk
On Self-Similarity of Top Production at Tevatron
Results of analysis of D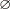 1.0 fb1 data on top-quark differential
cross section measurements
at the Fermilab Tevatron collider at
1.0 fb1 data on top-quark differential
cross section measurements
at the Fermilab Tevatron collider at 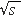 = 1960 GeV
in the framework of z-scaling approach are presented.
Flavour independence of the scaling function = 1960 GeV
in the framework of z-scaling approach are presented.
Flavour independence of the scaling function 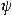 (z)
observed in pp and (z)
observed in pp and 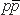 interactions over a wide collision
energy range interactions over a wide collision
energy range 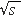 = 19-1960 GeV is verified.
This property of = 19-1960 GeV is verified.
This property of 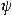 (z) was found for different hadrons from (z) was found for different hadrons from
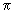 meson
up to meson
up to 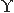 particle.
The flavour independence of particle.
The flavour independence of 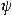 (z) is used as indication to self-similarity
of top-quark production.
A tendency to saturation of (z) is used as indication to self-similarity
of top-quark production.
A tendency to saturation of 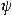 (z) at low z for top-quark is demonstrated.
The momentum fractions x1 of the incoming (anti)protons
as a function of the scaled transverse momentum pT/m and masses
of heavy mesons are studied.
We anticipate that data on low- and high-pT inclusive spectra
of top-quark production
at Tevatron and LHC energies could be of interest for verification
of the self-similarity over a wide range of masses and different
flavour content of produced particles. (z) at low z for top-quark is demonstrated.
The momentum fractions x1 of the incoming (anti)protons
as a function of the scaled transverse momentum pT/m and masses
of heavy mesons are studied.
We anticipate that data on low- and high-pT inclusive spectra
of top-quark production
at Tevatron and LHC energies could be of interest for verification
of the self-similarity over a wide range of masses and different
flavour content of produced particles.
|
E1-2012-13 (930.639)
Baatar Ts. et al.
A Possible Study of the Phase Transition in 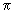 -C
Interaction at 40 GeV/c -C
Interaction at 40 GeV/c
In this paper we consider the momentum and angular characteristics of protons
and 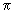 - mesons
produced in - mesons
produced in 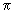 -C interactions at 40 GeV/c as a function of the
cumulative number nk
(or the four-dimensional momentum transfer t). Analysis carried out in this paper indicates possible
appearance of the phase transition of nuclear matter. -C interactions at 40 GeV/c as a function of the
cumulative number nk
(or the four-dimensional momentum transfer t). Analysis carried out in this paper indicates possible
appearance of the phase transition of nuclear matter.
|
P8-2012-14 (2.877.207)
Agapov N.N. et al.
Development and Reconstruction of VBLHEP Cryogenic System
for NICA Accelerator Complex (2012-2015)
A new NICA accelerator complex (Nuclotron-based Ion Collider fAcility),
presently under construction at JINR, will be, upon its completion in 2016,
among the most advanced research instruments of the physics community. The
facility is aimed to provide collider experiments with heavy ions up to
uranium (gold at the beginning stage) with a centre of mass energy up to 11 GeV/u
and an average luminosity up to 1027 cm-2  s-1.
The NICA cryogenics will be based on the modernized liquid
helium plant that was built in the early 1990s for the superconducting
synchrotron known as Nuclotron. The main goals of the modernization are
increasing of the total refrigerator capacity from 4000 to 8000 W at 4.5 K,
creating a new distribution system of liquid helium, and ensuring the
shortest possible cooldown time. These goals will be achieved by the use of
an additional 1000 l/h helium liquefier and «satellite» refrigerators
located in close proximity to the accelerator rings. We demonstrate helium
flow diagrams with major new components and discuss a system of liquid
nitrogen that will be used for shield refrigerating at 77 K and at the first
stage of cooling down of three accelerator rings with total length of about
1 km and «cold» mass of 220 t. s-1.
The NICA cryogenics will be based on the modernized liquid
helium plant that was built in the early 1990s for the superconducting
synchrotron known as Nuclotron. The main goals of the modernization are
increasing of the total refrigerator capacity from 4000 to 8000 W at 4.5 K,
creating a new distribution system of liquid helium, and ensuring the
shortest possible cooldown time. These goals will be achieved by the use of
an additional 1000 l/h helium liquefier and «satellite» refrigerators
located in close proximity to the accelerator rings. We demonstrate helium
flow diagrams with major new components and discuss a system of liquid
nitrogen that will be used for shield refrigerating at 77 K and at the first
stage of cooling down of three accelerator rings with total length of about
1 km and «cold» mass of 220 t.
|
P13-2012-16 (236.117)
Pepelyshev Yu.N. et al.
Experimental Estimations of the Kinetics Parameters of the IBR-2М Reactor by Stochastic Noises
Experimental investigations of stochastic fluctuations of pulse energy of
the IBR-2M reactor have been carried out which allowed us to obtain some of
the parameters of the reactor kinetics. At different levels of average power
a sequence of values of pulse energy was recorded with the calculation of
the distribution parameters. An ionization chamber with boron installed near
the active zone was used as a neutron detector. The research results allowed
us to estimate the average lifetime of prompt neutrons
 = (6.53 = (6.53 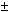 0.2) 0.2)  10-8 s, absolute power
of the reactor and intensity of the source of spontaneous
neutrons Ssp 10-8 s, absolute power
of the reactor and intensity of the source of spontaneous
neutrons Ssp 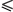 (6.72 (6.72 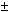 0.12) 0.12)  106 s-1.
It was shown that
the experimental results are close to the calculated ones. 106 s-1.
It was shown that
the experimental results are close to the calculated ones.
|
E1-2012-17 (605.859)
Piyadin S.M. et al.
First Extraction of the 3.42A GeV 12C Beam for Studies of Baryonic Matter at the Nuclotron
The results of the first extraction of the 3.42A GeV 12C beam at the Nuclotron
and its transportation to
the experimental area are presented. It is demonstrated that the beam parameters are sufficient for the first phase
of the experiments on the studies of the dense baryonic matter at the Nuclotron.
|
1-2012-18
Госткин М. И.
Измерение сечений реакций π±, p+C, π±, p ...... при 3-15 ГэВ/с для экспериментов нового поколенияки
Автореф. дис. ... канд. физ.-мат. наук
(rus)
|
E2-2012-19 (1.264.336)
Tokarev M.V., Dedovich T.G., Zborovsk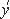 I. I.
Self-Similarity of Jet Production in pp and 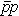 Collisions at RHIC, Tevatron, and LHC Collisions at RHIC, Tevatron, and LHC
Self-similarity of jet production in pp and 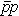 collisions is studied
in the framework of z scaling. Inclusive jet transverse momentum distributions measured by the
STAR Collaboration at RHIC, the CDF and D collisions is studied
in the framework of z scaling. Inclusive jet transverse momentum distributions measured by the
STAR Collaboration at RHIC, the CDF and D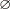 Collaborations at Tevatron, and the CMS and
ATLAS Collaborations at LHC are analyzed. The experimental spectra are compared with next-to-leading
order QCD calculations in pT and z presentations. It is shown that self-similar features of jet cross
sections manifested by the z scaling give strong restriction on the scaling function Collaborations at Tevatron, and the CMS and
ATLAS Collaborations at LHC are analyzed. The experimental spectra are compared with next-to-leading
order QCD calculations in pT and z presentations. It is shown that self-similar features of jet cross
sections manifested by the z scaling give strong restriction on the scaling function 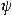 (z) at high z.
New results on energy and angular independence and asymptotic behavior of (z) at high z.
New results on energy and angular independence and asymptotic behavior of 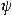 (z) are discussed. The obtained
results are considered as confirmation of self-similarity of jet production, fractality of hadron structure, and
locality of constituent interactions at small scales. (z) are discussed. The obtained
results are considered as confirmation of self-similarity of jet production, fractality of hadron structure, and
locality of constituent interactions at small scales.
|
P17-2012-23 (895.577)
Eremin R.A. et al.
Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Monocarboxylic Acid
Solutions in Decalin
Pure decalin solutions are investigated using the molecular dynamics
simulation method at different contents of stereoisomers. Limiting solutions
of monocarboxylic acids with different length of the hydrocarbon chains are
studied. A comparison of the features of the structural organization of
decalin stereoisomers in the vicinity of saturated (myristic and stearic)
and non-saturated (oleic) acid molecules is carried out. The limiting
partial molar volumes of the acids are calculated using radial distribution
functions. In contrast to earlier data on benzene, a significant difference
in the volumes of stearic and oleic acids is observed and explained by the
more complex molecular structure of decalin, which is sensitive to the
bending of the non-saturated acid molecule.
|
P9-2012-24 (2.683.863)
Denisov Yu.N. et al.
Computer Modeling of the Acceleration of Low Charge Krypton Ions in Cyclotron CYTRACK
The basic results of numeric simulations of krypton ion motion with
decreased charge in cyclotron CYTRACK are presented. Cyclotron CYTRACK is the first
world industrial cyclotron dedicated to produce the track membranes. Computer modeling
confirms the possibility of 84Kr+11 ion acceleration in the formed magnetic field with
increase of the magnetic field level by 1.6% on the sixth harmonic of the accelerating system.
Beam energy will be sufficient for exposure of the film with thickness 10  m. m.
|
6-2012-25
Иноятов А. Х.
Разработка метода прецизионной спектрометрии низкоэнергетических электронов, сопровождающих радиоактивный распад, и его применение в решении задач атомной и ядерной физики
Автореф. дис. ... доктора физ.-мат. наук
(rus)
|
14-2012-27
Рогачев А. В.
Молекулярная организация кремнийорганических дендримеров в растворах по данным малоуглового рассеяния нейтронов и рентгеновских лучей
Автореф. дис. ... канд. физ.-мат. наук
(rus)
|
P9-2012-28 (576.122)
Zhabitsky V.M.
Transient Beam Response in Synchrotrons with a Digital Transverse Feedback System
The transient beam response on an externally applied impulse force in synchrotrons
with a digital transverse
feedback system is studied. Experimental data from the LHC on damping of coherent transverse oscillations
excited by the discrete-time unit impulse are analysed. Good agreement on the measured and theoretically
predicted decrements has been obtained. A method of feedback fine tuning, based on measurements of bunch
response to harmonic excitation impulse, is discussed.
|
7-2012-29
Маслов В. А.
Экспериментальные исследования особенностей взаимодействия 6He и 6Li с ядрами
Автореф. дис. ... канд. физ.-мат. наук
(rus)
|
E14-2012-31 (390.955)
Kalabegishvili T. et al.
Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles by Blue-Green Algae Spirulina platensis
The synthesis of gold nanoparticles by one of the many popular
microorganisms - blue-green algae Spirulina platensis was studied. The complex of optical and
analytical methods was applied for investigation of experimental samples
after exposure to chloroaurate (HAuCl4) solution at different doses and
for different time intervals. To characterize formed gold nanoparticles
UV-vis, TEM, SEM, EDAX, and XRD were used. It was shown that after 1.5-2 days of exposure the extracellular formation of nanoparticles of spherical
form and the distribution peak within the interval of 20-30 nm took place.
To determine gold concentrations in the Spirulina platensis biomass, neutron activation analysis
(NAA) and atomic absorption spectrometry (AAS) were applied. The results
obtained evidence that the concentration of gold accumulated by Spirulina biomass is
rapidly growing in the beginning, followed by some increase for the next few
days. The obtained substance of Spirulina biomass with gold nanoparticles may be used
for medical, pharmaceutical, and technological purposes.
|
E10-2012-32 (397.595)
Isupov A.Yu.
New Software of the Control and Data Acquisition System
for the Nuclotron Internal Target Station
The control and data acquisition system for the Internal Target Station (ITS)
of the Nuclotron (LHEP, JINR) is implemented.
The new software is based on the
ngdp framework under the
Unix-like operating system FreeBSD to allow easy
network distribution of the on-line data collected from ITS,
as well as the internal target remote control.
|
E15-2012-33 (323.495)
Bogdanova L.N. et al.
Experimental Study of Nuclear Fusion Reactions in a pt System System
By means of muon catalysis we study the phenomena in a pt fusion,
which have been previously investigated in the only experiment and now are at the frontier of nuclear
few-body physics. The experiment is aimed at measuring the yields of the reaction products:  quanta,
conversion muons and e+e- pairs. As a result we plan to measure the
pt-fusion partial
product yields
(first time for e+e- pairs) with accuracy not worse than 10%, and this will enable us to obtain the
nuclear reaction rates in M1 and E0 transitions in A = 4 system.
quanta,
conversion muons and e+e- pairs. As a result we plan to measure the
pt-fusion partial
product yields
(first time for e+e- pairs) with accuracy not worse than 10%, and this will enable us to obtain the
nuclear reaction rates in M1 and E0 transitions in A = 4 system.
|
E15-2012-34 (1.232.243)
Didyk A.Yu., Wisniewski R.
Chemical Composition and Structural Phase Changes of Novel Synthesized Structure and of Pd Sample
under  -Quanta Irradiation in Dense Deuterium Gas -Quanta Irradiation in Dense Deuterium Gas
Studies have been carried out into the element composition of Pd and brass
with associated materials and of synthesized novel structure (ANNAWIT), placed in dense deuterium gas
in a special high-pressure chamber (HPC) under the pressure of 3 kbar and irradiated with
 -quanta
of energy up to 8.8 MeV. Using the methods of scanning electron microscopy, microelement chemical analysis
and X-ray diffraction, it was determined that in the absence of all HPC-forming materials in the chamber
volume and walls, the synthesized structure is largely composed of alumosilicates and Al and Si oxides with
high content of Ti compounds as rutile TiO2, Pd1.5D2. Considerable anomalies in the chemical
composition were found both on the surface and at large depth in a Pd specimen. The entire Pd surface turned
into a structure comprised of Pd clusters, Cu and Zn compounds, with a notable content of Mg, Al, S, Si, K, Ca, Ti,
and Fe compounds. Results of evaluative calculations, including computation of the Q-value, are presented for nuclear
reactions produced in a saturated with deuterium Pd specimen and dense deuterium gas under the action of -quanta
of energy up to 8.8 MeV. Using the methods of scanning electron microscopy, microelement chemical analysis
and X-ray diffraction, it was determined that in the absence of all HPC-forming materials in the chamber
volume and walls, the synthesized structure is largely composed of alumosilicates and Al and Si oxides with
high content of Ti compounds as rutile TiO2, Pd1.5D2. Considerable anomalies in the chemical
composition were found both on the surface and at large depth in a Pd specimen. The entire Pd surface turned
into a structure comprised of Pd clusters, Cu and Zn compounds, with a notable content of Mg, Al, S, Si, K, Ca, Ti,
and Fe compounds. Results of evaluative calculations, including computation of the Q-value, are presented for nuclear
reactions produced in a saturated with deuterium Pd specimen and dense deuterium gas under the action of
 -quanta, neutrons and protons of energies up to
En + Ep -quanta, neutrons and protons of energies up to
En + Ep
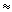 E E - -  W MeV generated
by deuteron fission. The obtained results can be explained by «collective effects» as chain
reactions caused by deuteron fission induced by protons (Ep > 3.39 MeV) and neutrons
(En > 2.25 MeV),
as well as by thermonuclear synthesis of deuterium atoms elastically scattered by protons of energies up to
EP < W MeV generated
by deuteron fission. The obtained results can be explained by «collective effects» as chain
reactions caused by deuteron fission induced by protons (Ep > 3.39 MeV) and neutrons
(En > 2.25 MeV),
as well as by thermonuclear synthesis of deuterium atoms elastically scattered by protons of energies up to
EP <  W MeV. W MeV.
|
E15-2012-35 (1.356.196)
Didyk A.Yu., Wisniewski R.
Phenomenological Nuclear Reaction Description in Deuterium-Saturated Palladium and Synthesized Structure
in Dense Deuterium Gas under  -Quanta Irradiation -Quanta Irradiation
The observed phenomena on changes of chemical compositions in previous reports [1,2]
allowed us to develop a phenomenological nuclear fusion-fission model with taking into consideration
the elastic and inelastic scattering of photoprotons and photoneutrons, heating of surrounding deuterium
nuclei, following D-D fusion reactions and fission of middle-mass nuclei by «hot» protons,
deuterons and various-energy neutrons. Such chain processes could produce the necessary number of neutrons,
«hot» deuterons for explanation of observed experimental results [1,2]. The developed
approach can be a basis for creation of deuterated nuclear fission reactors (DNFR) with high-density deuterium
gas and so-called deuterated metals. Also, the developed approach can be used for the study of nuclear reactions
in high-density deuterium or tritium gases and deuterated metals.
|
E5-2012-38 (214.779)
Zhidkov P.E.
On Weak Solutions of the Initial Value Problem for the Equation
utt=a(x, t)uxx + f(t, x,
u, ut, ux)
For the equation of the kind indicated in the title, it is assumed roughly speaking that
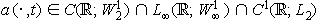 and
and 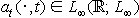 and that there exist 0 < a1 < a2 and a3 > 0
such that a1
and that there exist 0 < a1 < a2 and a3 > 0
such that a1 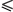 a(x, t) a(x, t) 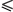 a2
and | a2
and | a(x, t)| a(x, t)| 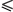 a3
for any a3
for any 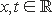 .
The function f is assumed to be continuously differentiable and satisfying
f(t, x, 0, r, s) .
The function f is assumed to be continuously differentiable and satisfying
f(t, x, 0, r, s) 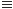 0.
The initial data are assumed to be in 0.
The initial data are assumed to be in 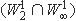 .
The existence and uniqueness of a local weak .
The existence and uniqueness of a local weak
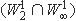 -solution is proved. In addition, in the special
case f(t, x, u, ut, ux) = -|uq-1|u,
q -solution is proved. In addition, in the special
case f(t, x, u, ut, ux) = -|uq-1|u,
q 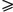 1 the
existence of a global weak solution is proved. 1 the
existence of a global weak solution is proved.
|
E1-2012-39 (63.061)
Kukhtin V.V. et al.
New Approaches for Searching for the Dirac Magnetic Monopole
Three new approaches, not applied earlier, are proposed to search
for the Dirac monopole - an object whose existence was proposed by P. Dirac more than
80 years ago to explain the electrical charge quantization.
The first approach assumes that the monopole must be accelerated by a magnetic field,
and such acceleration is constant in the magnetic field which is homogeneous and constant.
The conclusion about the object movement nature can be drawn by measuring the time marks for equidistant registering planes.
The second approach is supposed to reconstruct the movement trajectory in the
homogeneous and permanent electrical field, which is the circle or its part for the magnetic monopole.
The third approach is based on the constancy of energy losses by Dirac monopole due to
medium ionization in the multilayer passive dielectric tracking detectors placed in the homogeneous and
permanent electrical field.
|
4-2012-40
Литневский В. Л.
Описание реакций слияния-деления в рамках многомерного стохастического подхода, учитывающего ядерную оболочечную структуру
Автореф. дис. ... канд. физ.-мат. наук
(rus)
|
P13-2012-41 (1.216.862)
Ananiev V.D. et al.
Physical Start-up of the IBR-2 Modernized Reactor
Here we present the main results of the investigation of the IBR-2 reactor
after the completion of its modernization, which was carried out within the
framework of the program of the physical start-up of the reactor in
2010-2011 operated at a low power of up to 30 kW. The IBR-2 reactor was shut
down in 2006 since it reached its design service life limits. A considerable
part of the reactor main equipment was replaced except for a biological
shield, reactivity modulator and technological systems. According to the
results of the physical start-up of the modernized IBR-2 reactor the
critical loading of the core was 64 fuel assemblies. The remaining uncharged
five cells will ensure the reactor service life for no less than 20 years. The
efficiency of the control roads of the reactor safety system and the
operating speed of the emergency protection system units meet the nuclear
safety requirements. The imitation of the accidents connected with the
failures of various technological systems that maintain normal functioning
of the reactor has demonstrated that in all cases the reactivity insertion
rate is less than the acceptable value and the emergency protection system
units in any situation will decrease the reactor power to a safe level
during the period between pulses. The fast neutron pulse shape is close to
Gaussian with a halfwidth at maximum of (220 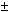 3) 3)  s. Mean square
values of the pulse energy fluctuations do not exceed 5%. The
technological systems of the reactor during the physical start-up operated
trouble free. s. Mean square
values of the pulse energy fluctuations do not exceed 5%. The
technological systems of the reactor during the physical start-up operated
trouble free.
|
P13-2012-42 (294.132)
Ananiev V.D. et al.
First Power of the IBR-2 Modernized Reactor
We present the main results of the investigation of the modernized IBR-2
reactor carried out within the framework of the program of the power
start-up of the reactor in 2011 operated at a power of up to rated 2 MW.
According to the results of the power start-up the reactor and its
technological systems operated without fail. The new safety control system
meets all design objectives and makes it possible to decrease the reactor
power to a safe level during the period between pulses. All fast feedbacks
(power, flow and isothermal effect) are negative at all levels of power and
sodium coolant flow rate through the core. Pulse energy fluctuations are
small (5.9% mean square) and considerably less than those of IBR-2
before its shutdown for modernization. The full width at half maximum is
(200 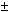 4) 4)  s, which is less than for IBR-2 in 2004
((245 s, which is less than for IBR-2 in 2004
((245 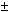 4) 4)  s). The peak pulse power is 1830 MW,
background between pulses 8.6% of mean power. The above-mentioned parameters allow the reactor to
maintain its safe and efficient operation at a power of 2 MW at a pulse
repetition rate of 5 s-1. s). The peak pulse power is 1830 MW,
background between pulses 8.6% of mean power. The above-mentioned parameters allow the reactor to
maintain its safe and efficient operation at a power of 2 MW at a pulse
repetition rate of 5 s-1.
|
4-2012-43
Кузякин Р. А.
Описание коллективного ядерного движения большой амплитуды в рамках квантового флуктуационно-диссипативного подхода
Автореф. дис. ... канд. физ.-мат. наук
(rus)
|
E14-2012-44 (236.669)
Mamedov T.N. et al.
Relaxation of the Shallow Acceptor Center in Germanium
Polarized negative muons were used to study relaxation mechanisms
of shallow acceptors in germanium. In p-type germanium at low temperatures
relaxation of the muon spin was observed, indicating that the muonic atom
(gallium-like acceptor center) formed via capture of the negative muon
by a host atom is in the paramagnetic state and its magnetic moment is
relaxing. The relaxation rate of the muon spin was found to depend on
the temperature and on the concentration of gallium impurity. We conclude that to
the relaxation of the magnetic moment of the Ga acceptor in Ge there
contribute both scattering of phonons and quadrupole interaction between
the acceptors. We estimate, for the first time, the hyperfine interaction
constant for the gallium acceptor in germanium as 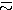 0.11 MHz. 0.11 MHz.
|
P13-2012-46 (475.174)
Bogdzel A.A. et al.
Experiment Automation System for a Neutron Powder Diffractometer
The study is concerned with the modernization of a detector system and a
control system of the neutron powder diffractometer (NPD) on the GEK-5
channel of the VVR-c reactor (Obninsk branch of the Karpov Institute of
Physical Chemistry). In the course of the work a PC-connected
hardware-software complex providing for data acquisition and accumulation,
as well as for experiment control, has been created. The main modules of the
automation system of NPD and the software complex Sonix+ developed in FLNP,
JINR, are briefly described. As a result of the modernization the luminosity
of the diffractometer has increased and the measurement process has become
fully automated.
|
4-2012-47
Антоненко Н. В.
Двойные ядерные системы в ядерных реакциях, делении и структуре ядра
Автореф. дис. ... доктора физ.-мат. наук
(rus)
|
P6-2012-48 (170.040)
Rakhimov A.V. et al.
Purification of Selenium from Thorium, Uranium,
Radium, Actinium and Potassium Impurities for the Low Background Measurements
The new generation of rare event searches experiments
requires a new level of very high radiopurity. Main impurities come from the
natural long-lived radionuclides Th, U, Ra, Ac and K. In the frame of this
field purification of Se polluted with those radioimpurities was carried out
taking special care of radiopurity of any reagent used. Аn instrumental
neutron activation analysis of bidistillated water, deionized water and
nitric acid was performed. These reagents were used during the process of
selenium purification from impurities of Th, U, Ra, Ac and K using the
reverse method. Distribution coefficients of 234Th, 230U,
223Ra, 225Ac on the cation-exchange resin DOWEX 50W-X8 in
different concentrations of selenium and nitric acid were experimentally
measured. The technique of selenium purification from Th, U, Ra, Ac and K
was developed. The developed technique of selenium purification has a simple
technology of execution and minimal number of reagents (water, nitric acid)
which possess a high degree of cleanliness. Operations applied during
purification (elution, evaporation) practically exclude losses of a target
product (chemical yields of Se > 99 %). Based on this technique test
purification of 100 g selenium was carried out. The efficiency of this
technique was confirmed by low background spectrometry of purified selenium
sample.
|
E17-2012-49 (1.075.823)
Tropin T.V. et al.
Kinetics of Cluster Growth in Polar Solutions of Fullerene:
Experimental and Theoretical Study of C60/NMP Solution
Theoretical models for describing the kinetics of fullerene cluster growth
in C60 solutions in N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP) are presented. First,
a detailed review of current state of experimental investigation of
C60/NMP is given. The relation between C60-NMP complex formation,
cluster growth and their impact on solvatochromism is discussed.
Next, we propose a theoretical approach for description of cluster growth
based on kinetic equations of segregation. Two modifications of basic
approach are given. First one treats cluster growth in a supersaturated
solution of C60, where new complex formation eventually limits growth
of aggregates. In the second model a two-step process of cluster growth is
considered: complex formation and cluster growth. The solution of
C60-NMP complexes is supersaturated, while initial, «free» C60
does not aggregate. For each model a procedure for obtaining parameters is
proposed and the parameters values are obtained.
|
P15-2012-50 (3.348.567)
Didyk A.Yu., Wisniewski R.
Synthesis of Novel Structures in Dense Deuterium
and Deuterium Saturated Palladium
at Nuclear Reactions Induced by  -Quanta -Quanta
Elemental composition studies of Pd sample irradiated by
 -quanta in dense deuterium gas of continuous spectrum with the boundary 8.8 MeV
energy were carried out. Significant anomalies in the structure and chemical composition are obtained.
Considerable changes are observed at both ends of the Pd rod as blowouts of molten metal with complex
element composition. A short description of the phenomenological model of nuclear reactions leading to
the observed anomalies is presented. -quanta in dense deuterium gas of continuous spectrum with the boundary 8.8 MeV
energy were carried out. Significant anomalies in the structure and chemical composition are obtained.
Considerable changes are observed at both ends of the Pd rod as blowouts of molten metal with complex
element composition. A short description of the phenomenological model of nuclear reactions leading to
the observed anomalies is presented.
|
P2-2012-52 (571.731)
Konopleva N.P.
A.Z.Petrov and His Times: My Reminiscences
The situation in geometry, relativity theory and theoretical physics,
which was in the 60s-70s of the 20th century in the USSR, is
under discussion. The author tells us about Petrov's works on General
Relativity, and his contribution to scientific research organization in the above-mentioned fields.
|
P16-2012-53 (281.000)
Ambrozova I. et al.
LET Spectrometry of the Clinical 12C Ion Beams
The sets of track etched detectors for the linear energy transfer (LET) spectrometry were
exposed in 12C 135, 290 and 400 MeV/amu ion beams at the HIMAC installation at NIRS (Chiba, Japan).
LET spectra were measured at various depths in 12C ion beams through the Bragg peak area up to the
region of fragmentation behind the Bragg peak.
In the paper LET spectra measured with track etched detectors TD-1, at the beams axis along the depth up to the region
behind the Bragg peak are presented.
The dosimetric values calculated from measured LET spectra are given. The depth distributions of absorbed dose and biological
weighted effective dose for radiation therapy are calculated. Relative biological weighted efficiency of 12C beams at the
various depths is estimated. The depth-dose distribution calculated from LET spectra is in a good agreement with reference
measurements in HIMAC.
|
E14-2012-54 (2.410.156)
Iacobescu G.E., Balasoiu M., Bica I.
Investigation of Magnetorheological Elastomer
Surface Properties by Atomic Force Microscopy
Magnetorheological elastomers consist of a natural or synthetic
rubber matrix interspersed with micron-sized ferromagnetic particles. The
magnetoelastic properties of such a composite are not merely a sum of
elasticity of the polymer and stiffness and magnetic properties of the
filler, but also the result of a complex synergy of several effects,
relevant at different length scales and detectable by different techniques.
In the present work we investigate the microstructures, the surface magnetic
properties and the elastic properties of new isotropic and anisotropic
magnetorheological elastomer prepared using silicone rubber and soft
magnetic carbonyl iron microspheres. The measurements were performed by
atomic force microscopy in the following modes: standard imaging - non-contact
atomic force microscopy, magnetic force microscopy and nanoindentation. A
comparative study for the samples with different particle concentrations and
strength of magnetic field applied during the polymerization process is
developed.
|
14-2012-56
Бобриков И. А.
Структурное и магнитное мезоскопическое фазовое расслоение в сложных оксидах переходных металлов
Автореф. дис. ... канд. физ.-мат. наук
(rus)
|
E7-2012-58 (178.277)
Oganessian Yu. Ts. et al.
New Insights into the 243Am + 48Ca Reaction Products Previously
Observed in the Experiments on Elements 113, 115, and 117. II
We continued experiments on measuring excitation functions of the
reaction 243Am + 48Ca and investigation of radioactive properties of isotopes of element
115 that were started in 2010-2011, now at two projectile energies of 241 and 254 MeV. At the lowest
energy of 48Ca, we registered seven decay chains of 288115 and three decay chains of the
2n-evaporation product, 298115, which was also observed previously in the reaction
249Bk + 48Ca as the daughter nucleus of the decay of 293117. At the beam energy of
254 MeV one decay chain of 287115 was detected.
Altogether thirty-one decay chains originating from 288115 were established as the product of the
3n-evaporation channel by measuring the excitation function at five excitation energies of the compound nucleus
291115. The decay properties of all the newly observed nuclei 287115, 288115 and their descendant
nuclides are in full agreement with those we measured in 2003.
The 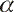 -particle energies and decay times of the isotopes 289115, 285113, and
281Rg produced
in cross reactions with the two target nuclei 243Am and 249Bk agree well to provide cross bombardment
evidence for the discovery of the new elements 113, 115, and 117. -particle energies and decay times of the isotopes 289115, 285113, and
281Rg produced
in cross reactions with the two target nuclei 243Am and 249Bk agree well to provide cross bombardment
evidence for the discovery of the new elements 113, 115, and 117.
|
P18-2012-59 (1.248.081)
Kravets L.I. et al.
Research on the Surface and Electrochemical Properties of Polypropylene Track Membrane Modified
by Non-Polymerizing Gas Plasma
Surface and electrochemical properties of polypropylene track membrane treated by plasma
of nitrogen, air as well as oxygen have been investigated. The influence of the plasma-forming gas composition
on the morphology of its surface is studied. It has been found that the micro-relief of the surface of the
membranes formed during the gas-discharge etching changes. The effect of the non-polymerizing gas plasma,
besides causing oxidation of the membrane surface layer, leads to formation of oxygen-containing functional,
basically carbonyl and carboxyl, groups. It is shown that increase in the roughness of the membrane surface and
its hydrophilization cause improvement of wettability. In addition, the presence of polar groups in the surface
layer of the membranes causes change of their hydrodynamic and electrochemical properties - the water permeability
and electric conductivity of the modified membranes raise.
|
P1-2012-60 (436.363)
Merts S.P., Razin S.V., Rogachevsky O.V.
Accumulation of Spatial Charge in the Time-Projection Chamber of the Multipurpose Detector
The article presents results of numerical simulation of spatial positive
charge accumulation in the TPC of Multipurpose Detector at NICA, JINR.
Based on the spatial distribution of the charges problem of calculating
the electrostatic potential of field created by these charges is solved.
The radial, angular and axial distortions of electrons movement from the
point of ionization to readout planes are calculated.
|
E15-2012-61 (943.624)
Sabirov B. et al.
Nuclear Processes Induced by Muon Decay at the K-Orbit of Muonic Atom
Results are presented of an experimental study of processes taking place in the
case of muons stopping in nuclei. The aim of the experiment consists in investigating the possibility
of a nucleus being excited when a muon on the K-orbit decays. The uniqueness of this process is that
the nucleus, happening to be in the electromagnetic field of the muon occupying the lowest atomic orbit
of angular momentum 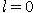 , is jolted, when the muon decay , is jolted, when the muon decay 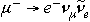 occurs, and it mainly undergoes monopole excitation.
The experiment aimed at searching for nuclear excitation related to a bound muon is based on the registration
of coincidences between electrons from
occurs, and it mainly undergoes monopole excitation.
The experiment aimed at searching for nuclear excitation related to a bound muon is based on the registration
of coincidences between electrons from  decays
and decays
and  quanta from nuclear transitions.
An experimental installation MEGA has been created, that involves a set of scintillation counters
for identifying muons stopping in the target enriched with powder-like samarium dioxide
Sm2O3, a Ge(Li) quanta from nuclear transitions.
An experimental installation MEGA has been created, that involves a set of scintillation counters
for identifying muons stopping in the target enriched with powder-like samarium dioxide
Sm2O3, a Ge(Li)  detector with a sensitive volume
~ 50 cm3
and a Cherenkov counter made of TF-1 lead glass. The experiment was carried out with the muon beam in
the low-background hall of the Phasotron of the JINR Laboratory of Nuclear Problems. The total number
of muons that stopped in the target permitted to determine the upper limit for E0 excitation
in the 152Sm
nucleus to be w(E0) < 1.5 detector with a sensitive volume
~ 50 cm3
and a Cherenkov counter made of TF-1 lead glass. The experiment was carried out with the muon beam in
the low-background hall of the Phasotron of the JINR Laboratory of Nuclear Problems. The total number
of muons that stopped in the target permitted to determine the upper limit for E0 excitation
in the 152Sm
nucleus to be w(E0) < 1.5  10-3, which is inferior
to the level of the theoretical estimate
( 10-3, which is inferior
to the level of the theoretical estimate
(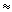 3 3  10-4). The isomeric shift of the
121.78 keV level in the nucleus has been measured
in the presence of a muon on the K-orbit of a muonic atom: 10-4). The isomeric shift of the
121.78 keV level in the nucleus has been measured
in the presence of a muon on the K-orbit of a muonic atom:
 Eis = 820 Eis = 820 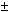 40 eV.
The search for monopole excitation of a nucleus related to the decay of a bound muon is to be continued
with the use of improved equipment and muon beams of higher intensity. 40 eV.
The search for monopole excitation of a nucleus related to the decay of a bound muon is to be continued
with the use of improved equipment and muon beams of higher intensity.
|
E6-2012-62 (169.713)
Izosimov I.N. et al.
Chemiluminescence Initiated by Laser-Induced Excitation of Lanthanide and Actinide Ions in Aqueous Solutions
Data on luminol chemiluminescence in solutions containing Sm(III), U(IV),
and Pu(IV) are presented. Chemiluminescence was induced by multiquantum excitation of lanthanide and actinide
ions in the range of 4f- and 5f-electron transitions by the schemes: two steps - one color and two steps - two
colors with the use of dye lasers. We observed chemiluminescence of chemiluminogen (luminol) caused by multiquantum
excitation of lanthanides and actinides in aqueous solutions by laser radiation. A multistep scheme of
chemiluminescence excitation makes this procedure not only highly sensitive but also highly selective procedure
of detection of substances.
|
P15-2012-63 (471.161)
Didyk A.Yu., Wisniewski R.
Nuclear Reactions in Palladium Saturated with Deuterium
and Rhenium in Dense Deuterium Gas under Irradiation
by  -Quanta of Continuous Spectrum with Boundary 23 MeV Energy -Quanta of Continuous Spectrum with Boundary 23 MeV Energy
Elemental composition studies of Pd and Re samples irradiated by
 -quanta in dense deuterium gas of continuous spectrum with the boundary
23 MeV energy were carried out.
Significant anomalies in the structure and
chemical composition are obtained. Considerable changes are observed at both
ends of the Pd and Re wire as blowouts of molten metal with complex element
composition, resembling congealed Solar protuberances. The cracky surfaces
of the Pd and Re wires were covered with 1-2 -quanta in dense deuterium gas of continuous spectrum with the boundary
23 MeV energy were carried out.
Significant anomalies in the structure and
chemical composition are obtained. Considerable changes are observed at both
ends of the Pd and Re wire as blowouts of molten metal with complex element
composition, resembling congealed Solar protuberances. The cracky surfaces
of the Pd and Re wires were covered with 1-2  m particles predominantly
composed of rhenium oxide RexCy. These particles had been
crystallized into small hexagonal crystallites near the cracks in the
palladium. The rhenium surface was covered by a thick layer with a large
carbon concentration. A short description of the phenomenological model of
nuclear reactions leading to the observed anomalies is presented. m particles predominantly
composed of rhenium oxide RexCy. These particles had been
crystallized into small hexagonal crystallites near the cracks in the
palladium. The rhenium surface was covered by a thick layer with a large
carbon concentration. A short description of the phenomenological model of
nuclear reactions leading to the observed anomalies is presented.
|
E15-2012-65 (341.134)
Karamian S.A.
Threshold and Spin Factors in the Yield of Bremsstrahlung-Induced Reactions
Relative yields of photon-induced reactions are systematized in a
function of the threshold parameter for moderately heavy targets at the bremsstrahlung
end-point energy lower than 30 MeV. Regular dependence is established for the group
of ( , n), ( , n), ( , p),
and ( , p),
and ( , d) reactions while the yields
of ( , d) reactions while the yields
of ( , , 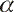 )
and ( )
and ( , 2n)
reactions deviate from the regularity.
Physical conclusions are discussed and possible application of this systematics for
data processing is proposed. In particular, the constituent threshold and spin factors
in the isomer-to-ground state ratio could be separately isolated. For spin dependence
of the yields, a new regularization parameter is introduced and previously hidden peculiarities are concluded. , 2n)
reactions deviate from the regularity.
Physical conclusions are discussed and possible application of this systematics for
data processing is proposed. In particular, the constituent threshold and spin factors
in the isomer-to-ground state ratio could be separately isolated. For spin dependence
of the yields, a new regularization parameter is introduced and previously hidden peculiarities are concluded.
|
E13-2012-68 (774.907)
Anfimov N.V. et al.
Shashlyk EM Calorimeter Prototype Read Out by MAPD with Superhigh Pixel Density for COMPASS II
A new-generation high-granularity Shashlyk EM calorimeter read out by micropixel
avalanche photodiodes (MAPD) with precision thermostabilization based on the Peltier element was designed,
constructed and tested. MAPD-3N with a superhigh pixel density of 1.5  104 mm-2
and an area
of 3 104 mm-2
and an area
of 3 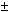 3 mm manufactured by the Zecotek Company were used in the photodetector unit. 3 mm manufactured by the Zecotek Company were used in the photodetector unit.
|
E13-2012-69 (261.651)
Gapienko V.A. et al.
Test of Strip Readout MRPC Equipped with Amplifier Discriminator Based on the NINO Chip
The use of wide strips instead of pads as readout electrodes in a multigap
resistive plate chamber (MRPC) helps to reduce essentially a number of FEE channels. However,
a strip being a transmission line, requires correct matching with an end terminator that leads
to a certain problem in applying already existing FEE in which the time-width correction method
is realized to read pads. Here we describe our attempts to use two different amplifier discriminators
based on the NINO chip to read 25 mm wide strips in six- and ten-gap timing MRPCs. Tests have been carried
out at the IHEP U-70 PS (Protvino).
|
9-2012-71
Трубников Г. В.
Синхротрон релятивистских тяжелых ионов НУКЛОТРОН в ускорительном комплексе NICA
Автореф. дис. ... доктора физ.-мат. наук
(rus)
|
11-2012-72
Киян И. Н.
Математическое моделирование режимов работы многоцелевого изохронного циклотрона АИЦ-144
Автореф. дис. ... канд. физ.-мат. наук
(rus)
|
E7-2012-73 (343.491)
Fomichev A.S. et al.
Long-Range Plans for Research with Radioactive Ion Beams at JINR
Dubna Radioactive Ion Beams (DRIBs) is a general name for initiative to develop a complex of
experimental facilities in the Flerov Laboratory of Nuclear Reactions, which should enable world-class research
with Radioactive Ion Beams at JINR (Dubna, Russia). The first stage of this initiative (DRIBs-1) operates
successfully. However, to meet the requests of the modern research, a new project DRIBs-3 is now being developed.
It is based on the in-flight RIB production technique augmented with an ISOL-type second stage. The new
fragment-separator ACCULINNA-2 comprising important part of the prospective facility is now under construction
with an expected commissioning date in 2015. The long-range plans for experimental research at DRIBs-3 and the
program for further development of this facility are discussed.
|
17-2012-74
Бънзарова Н. Ж.
Конечноразмерное подобие и универсальность в решеточных процессах переноса
Автореф. дис. ... канд. физ.-мат. наук
(rus)
|
P15-2012-75 (744.913)
Didyk A.Yu., Wisniewski R.
Changes Observed in the Surfaces, Bulk Properties
and Chemical Composition of Vanadium and Stainless Steel Specimens
Irradiated in Dense Gaseous Deuterium by  -Quanta of Threshold Energy 23 MeV -Quanta of Threshold Energy 23 MeV
Studies have been carried out into the changes of properties and element
composition of vanadium (V) and stainless steel (SS) specimens irradiated in
gaseous deuterium under the pressure 2 kbar by  -quanta of
continuous spectrum with the boundary energy 23 MeV. Considerable changes
are observed in the surface structure and bulk properties of the irradiated V and SS specimens,
as was in the earlier authors studies, and in the
element composition. The phenomenological model of nuclear reactions leading
to the observed element composition of V and SS is described. -quanta of
continuous spectrum with the boundary energy 23 MeV. Considerable changes
are observed in the surface structure and bulk properties of the irradiated V and SS specimens,
as was in the earlier authors studies, and in the
element composition. The phenomenological model of nuclear reactions leading
to the observed element composition of V and SS is described.
|
E10-2012-78 (101.733)
Makankin A.M. et al.
A Direct Timing Method for the Two-Dimensional
Precision Coordinate Detectors Based on Thin-Walled Drift Tubes
The results of a study of the longitudinal spatial resolution of 2 m long
straw tubes by means of the direct timing method (DTM) are presented. The feasibility of achieving
a coordinate resolution (r.m.s.) better than 9 mm over full length of the straw is demonstrated.
The spatial resolution insignificantly changes when measured by detecting gammas from a
55Fe gamma-ray source or minimum ionizing particles from a 106Ru source.
The use of the same type of FEE for data taking both for measuring the drift time of ionization electrons
and propagation of a signal along the anode wire allows one to construct a two-dimensional detector for
precision coordinate measurements.
|
9-2012-80
Карпинский В. Н.
Системы питания и эвакуации энергии в быстроциклирующих сверхпроводящих синхротронах
Автореф. дис. ... канд. тех. наук
(rus)
|
9-2012-81
Бутенко А. В.
Ускорение пучков тяжелых ионов с массовым числом более 100 в сверхпроводящем синхротроне Нуклотрон
Автореф. дис. ... канд. тех. наук
(rus)
|
P13-2012-82 (916.003)
Morozov V.A., Morozova N.V.
Time Correlation of Noise Pulses in a PMT
Two types of time correlation of noise pulses caused by the PMT photocathode
and dynodes are established using the autocorrelation delayed-coincidence time spectrometer.
Time distributions of noise pulses in the XP2020, XP2232B, XP1021, FEU-85, FEU-87, FEU-93, and FEU-130
photomultiplier tubes are investigated. An exponential time component of noise pulses with a nanosecond
scintillation time is found in some types of PMTs.
|
P10-2012-83 (137.467)
Zlokazov V.B., Utyonkov V.K.
Optimum Confidence Interval in the Analysis of Exponentially Distributed Rare Events
In the analysis of rare events a typical question is as follows: does an observed
event ti belong to distribution function with some known parameter?
The answer is provided by a
region of the (0, t) axis (a confidence interval), inside which the event
ti occurs with an a
priori probability P.
It is appropriate to construct an optimal confidence interval (OCI) satisfying the following requirements
which secure that this interval contains the observed random quantity most probably: 1) the length of such an
interval should be minimal; 2) the probability within such an interval should be maximum; 3) the ratio of the
probabilities of the null hypothesis and its alternative should be maximum.
The OCI does not exist for any arbitrary distribution function. However, one can construct such an OCI for
the exponential distribution F(t, T) = 1 - exp(-t/T),
where it equals [0.2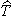 ]. Here ]. Here 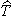 is an
estimate of T. The exponential distribution function is of fundamental importance in the physics of the
radioactive decays. The OCI has advantages over usual confidence intervals, since it provides a smaller sum
of the Type I and the Type II errors in testing the hypotheses. is an
estimate of T. The exponential distribution function is of fundamental importance in the physics of the
radioactive decays. The OCI has advantages over usual confidence intervals, since it provides a smaller sum
of the Type I and the Type II errors in testing the hypotheses.
|
E15-2012-84 (101.124)
Karamian S.A.
Yield of Bremsstrahlung Induced Reactions as a Probe of Nucleon-Nucleon Correlations in Heavy Nuclei
Relative yields of ( , , 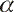 )
reactions could serve as a probe to verify the
theoretical models which assume total alpha-clustering, or multiquark objects in heavy nuclei.
A deficit of data on the ( )
reactions could serve as a probe to verify the
theoretical models which assume total alpha-clustering, or multiquark objects in heavy nuclei.
A deficit of data on the ( , , 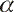 )
process probability must be covered in relatively
simple activation experiments. Five concrete reactions are distinguished providing favorable conditions
for detection of the low-probability reaction branch ( )
process probability must be covered in relatively
simple activation experiments. Five concrete reactions are distinguished providing favorable conditions
for detection of the low-probability reaction branch ( , ,
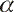 ). The following requirements must
be satisfied: the target species available in an enriched form, the convenient properties of the product
activity, and reasonably soft background restrictions. In the present experiment with bremsstrahlung at
Ee = 23 MeV, new results are successfully obtained for ( ). The following requirements must
be satisfied: the target species available in an enriched form, the convenient properties of the product
activity, and reasonably soft background restrictions. In the present experiment with bremsstrahlung at
Ee = 23 MeV, new results are successfully obtained for ( , ,
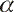 ) reactions in two cases and
upper limits are deduced for three other ones. Much lower probability of ( ) reactions in two cases and
upper limits are deduced for three other ones. Much lower probability of ( , ,
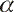 ) compared to
( ) compared to
( , p) reactions is proved. Alpha-clustering in heavy nuclei is not supported. , p) reactions is proved. Alpha-clustering in heavy nuclei is not supported.
|
P1-2012-85 (319.359)
Yurevich V.I., Fomenko K.A.
Fission and Fragmentation of 208Pb Nuclei in Collisions
with Gold Nuclei at Energy of 158 GeV/nucleon
Fission and fragmentation of ultrarelativistic 208Pb nuclei in
collisions with gold nuclei were studied with beam of SPS/CERN at an energy of
158 GeV/nucleon. Detectors of target area of NA45/CERES spectrometer were
used in the measurements. The obtained magnitude of the fission cross section is
(301 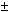 44) mb where approximately 77% of the events are due to
electromagnetic interactions of the colliding nuclei and the rest part is the
contribution of peripheral nuclear interactions. Spallation of the lead
nuclei with production of heavy fragments occurs only in collisions with
values of impact parameter b > 10 fm. Total disintegration of the lead
nuclei into intermediate mass fragments and light particles is observed in
some peripheral collisions. 44) mb where approximately 77% of the events are due to
electromagnetic interactions of the colliding nuclei and the rest part is the
contribution of peripheral nuclear interactions. Spallation of the lead
nuclei with production of heavy fragments occurs only in collisions with
values of impact parameter b > 10 fm. Total disintegration of the lead
nuclei into intermediate mass fragments and light particles is observed in
some peripheral collisions.
|
P11-2012-86 (528.445)
Dikusar N.D.
Piecewise Polynomial Approximation of the Sixth Order with Automatic Knots Detection
Coefficients of a local segment model for piecewise polynomial approximation
of the sixth order are evaluated using values of the function and of its first derivative at
three knots of the support. Formulae for coefficients of the function expansion in degrees of
(x - x0) on a three-point grid are obtained within the framework of the recently
proposed basic
element method. An algorithm for automatic knot detection is developed. Numerical calculations applying
quite complicated tests have shown high efficiency of the model with respect to the calculation stability,
accuracy and smoothness of approximation.
|
P11-2012-87 (108.685)
Melezhik A.V.
Speeding Up Matrix Element Computations by Means of MPI Parallel Programming
The solution of some quantum-mechanical problems asks computing large sets of matrix
elements involving non-factorable two-dimensional integrals. In the present paper we discuss effective means,
using MPI parallel programming, for speeding up the computation of large sets of such matrix elements.
To make sound comparison of the computing times, we have developed the sequential code Potential_PC
and the parallel code Potential_MPI, able to solve the problems of interest on a personal computer and
on a multi-core cluster, respectively. Investigation of case study problems involving matrix elements of
specific operators over oscillatory bases showed a gain of CPU time exceeding two orders of magnitude.
|
10-2012-88
Акишина Т. П.
Развитие методов идентификации электронов для детектора переходного излучения эксперимента СВМ
Автореф. дис. ... канд. физ.-мат. наук
(rus)
|
P13-2012-93 (1.545.735)
Davkov K.I. et al.
Straw-Based Coordinate Muon Chambers
The article considers a prototype module with sensitive dimensions of
2 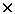 0.5 m based on 2 m long straw tubes which preserves its geometrical dimensions up to
the pressure of 4 bar independently of the ambient temperature and humidity. The suggested technique
provides a possibility of constructing relatively low-cost planar modules by using straw tubes as long
as needed for constructing large area detectors at colliders or other field experiments by assembling
them in a common coordinate detector with a user-specified acceptance. The distinguishing feature of a
detector is its good radiation hardness, low radiation thickness and a possibility of optimizing the detector
operation mode in a large range of gas pressure. 0.5 m based on 2 m long straw tubes which preserves its geometrical dimensions up to
the pressure of 4 bar independently of the ambient temperature and humidity. The suggested technique
provides a possibility of constructing relatively low-cost planar modules by using straw tubes as long
as needed for constructing large area detectors at colliders or other field experiments by assembling
them in a common coordinate detector with a user-specified acceptance. The distinguishing feature of a
detector is its good radiation hardness, low radiation thickness and a possibility of optimizing the detector
operation mode in a large range of gas pressure.
|
E7-2012-95 (138.715)
Volkov V.V., Cherepanov E.A.
Formation of Nuclear Molecules in Cluster Radioactivity.
On Interpretation of the Cluster Radioactivity Mechanism
The basis for cluster radioactivity is the property of nuclei of light isotopes of
elements heavier than lead to spontaneously form clusters - nuclei of light elements - from valence nucleons,
which gives rise to asymmetric nuclear molecules. The cluster formation proceeds through successive excitation-free
transfer of valence nucleons to the 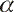 particle and to subsequent light nuclei. Nuclear molecule formation
is accompanied by a considerable amount of released energy, which allows quantum-mechanical penetration of the
cluster through the exit Coulomb barrier. particle and to subsequent light nuclei. Nuclear molecule formation
is accompanied by a considerable amount of released energy, which allows quantum-mechanical penetration of the
cluster through the exit Coulomb barrier.
|
E19-2012-96 (373.238)
Belov O.V. et al.
The Role of the Bacterial Mismatch Repair System in SOS-Induced Mutagenesis: A Theoretical Background
A theoretical study is performed of the possible role of the methyl-directed
mismatch repair system in the ultraviolet-induced mutagenesis of
Escherichia coli bacterial cells. For this purpose, a mathematical model of the bacterial
mismatch repair system is developed. Within this model, the key pathways of
this type of repair are simulated on the basis of modern experimental data
related to its mechanisms. Here we have modelled in detail five main
pathways of DNA misincorporation removal with different DNA exonucleases.
Using our calculations, we have tested the hypothesis that the bacterial
mismatch repair system is responsible for the removal of the nucleotides
misincorporated by DNA polymerase V (the UmuD'2C complex) during
ultraviolet-induced SOS response. For the theoretical analysis of the
mutation frequency, we have combined the proposed mathematical approach with the
model of SOS-induced mutagenesis in the E.coli bacterial cell developed earlier.
Our calculations support the hypothesis that methyl-directed
mismatch repair influences the mutagenic effect of ultraviolet radiation.
|
P11-2012-99 (135.563)
Amirkhanov I.V. et al.
Analytical and Computational Investigations
of Solutions of Scattering Problem for the Quasipotential Equation
Investigation of solutions of a scattering problem is carried out
for the quasipotential equation with piecewise-constant potentials at
various values of the parameters of the problem. The comparative analysis of
the solutions of the quasipotential equation with the solutions of
Schr dinger equation is performed. dinger equation is performed.
|
E3-2012-100 (397.265)
Sukhovoj A.M. et al.
General Trend and Local Variations of Neutron Resonance Cascade Gamma-Decay Radiative Strength Functions
A new hypothesis on dependence of the form of the radiative strength functions of
electric and magnetic dipole gamma transitions in heated nucleus on the excited level density was
suggested and tested experimentally. For this purpose, the region of possible values of random values
of the level density and radiative strength functions which precisely reproduced experimental intensity
of two-step cascades for 41 nuclei from 40K to 200Hg was determined. It was obtained that the
suggested hypothesis can provide the maximal increase of radiative strength functions values by order of
magnitude in comparison with existing notations as a result of collective effects enhancement. This result
points to the necessity to take into account this possibility in existing and future models of radiative
strength functions.
|
P4-2012-101 (224.366)
Pupyshev V.V.
Scattering of a Slow Quantum Particle by a Central Short-Range Potential
In the present work the linear version of the variable phase
approach to the potential scattering is added by a new asymptotical
method. This method is adopted for a quantum mechanical analysis and
the construction of explicit low-energy approximations for the
partial phase shifts and radial components of the wave function
describing the scattering of a quantum particle by a central
short-range potential. The construction of these approximations is
reduced to the solution of the recurrence chain of energy
independent systems, each system contains two linear first order
differential equations. A special attention is paid to physical
interpretation of all used functions and the optimization of their
numerical analysis.
|
D18-2012-102 (288.926)
Ignatenko O.V. et al.
Changes of Nitrides Characteristics in Li-N System Synthesized at Different Pressures
Lithium nitride samples were obtained in Li-N system at nitrogen
pressure 1-10 atm. Energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) spectrum of Li-N samples subjected to
decomposition demonstrates that lithium nitride is converted into carbonate revealing predominant
content of carbon and oxygen. When lithium nitride is being synthesized at positive pressure of nitrogen,
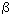 -modification, which can be achieved at pressure 500 times higher,
is formed; this allows one to
hypothesize the minimum pressure required to create a high-pressure phase. The increase in carbon content
with increasing synthesis pressure of lithium nitride confirms the change in stoichiometry of its structure
formed with high nitrogen content. -modification, which can be achieved at pressure 500 times higher,
is formed; this allows one to
hypothesize the minimum pressure required to create a high-pressure phase. The increase in carbon content
with increasing synthesis pressure of lithium nitride confirms the change in stoichiometry of its structure
formed with high nitrogen content.
|
E14-2012-103 (90.008)
Stan C. et al.
Investigations of a CoFe2O4-Ferrofluid Structure by Means of Magnetic Measurements
Analysis of experimental results of a water based CoFe2O4 ferrofluid sample by means
of magnetic measurements in the temperature range from 80 to 350 K is presented. For the experimental magnetization
curves, the fitting magnetogranulometric methods based on the Langevin model for a log-normal distribution of
the magnetic particle diameters were considered for two temperature values of 80 and 300 K.
|
P14-2012-104 (113.634)
Didyk A.Yu. et al.
Thermal Processes in Multi-Layered Second Generation HTSC under Swift Heavy Ion Irradiation
On the basis of the thermal spike model, the estimations with regard to ribbons of the
second generation Ag/YBaCuO/MgO/Hastelloy HTSC under irradiation by Ar, Kr and Xe ions with an energy of about
1.2 MeV/a.m.u. have been carried out. The obtained results have been compared with available experimental data.
In addition, the possibility of processes such as melting, recrystallization, amorphization and other phase
transitions in multi-layered structures under ion irradiation has been studied.
|
P4-2012-105 (195.638)
Lukyanov V.K. et al.
A Modeling of the Pion-Nucleus Microscopic Optical Potential at Energies of (3,3)-Resonance and In-Medium Effect
on the Pion-Nucleon Amplitude of Scattering
Analysis is performed of differential cross sections of elastic scattering of pions on
different nuclei at energies between 130 and 290 MeV. To this end the pion-nucleus microscopic optical
potential (OP) was applied. Such an OP was constructed using the Glauber theory and defined by the target
nucleus density distribution of bare nucleons and by the elementary 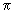 N-amplitude of scattering.
The pion-nucleus cross sections are calculated by numerically solving the corresponding relativistic
wave equation. The three parameters of the N-amplitude of scattering.
The pion-nucleus cross sections are calculated by numerically solving the corresponding relativistic
wave equation. The three parameters of the 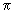 N scattering amplitude, the total cross section,
the ratio of real to imaginary part of the forward N scattering amplitude, the total cross section,
the ratio of real to imaginary part of the forward 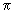 N-amplitude, and the slope parameter, were
fit to the data on the respective pion-nucleus cross sections. Thus, comparing the sets of «free»
parameters to those obtained from pion-nucleus scattering data, the in-medium effect on the N-amplitude, and the slope parameter, were
fit to the data on the respective pion-nucleus cross sections. Thus, comparing the sets of «free»
parameters to those obtained from pion-nucleus scattering data, the in-medium effect on the 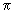 N scattering
amplitude is discussed. N scattering
amplitude is discussed.
|
E15-2012-107 (969.474)
Demin D.L. et al.
Gamma Spectrometer for Studying the MCF Reactions
A gamma spectrometer composed of two identical
BGO-based gamma detectors and associated electronics is described.
The main characteristics of the spectrometer are its high detection
efficiency in the energy range of gamma rays
E 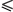 30 MeV and low sensitivity
to the accidental background.
A distinctive feature of the detector is a plastic
scintillator, which surrounds BGO crystal and is viewed by
the same photomultiplier tube.
This provides effective protection of the detector
against the charged particle background.
The detector design allows for a compact experimental
setup with a large solid angle of gamma-ray registration.
The simulation of the spectrometer response function
%on the basis of a software package
has been performed and
experimentally verified using GEANT4 program.
The spectrometer was used in a search for the rare muon-catalyzed
fusion (MCF) reaction
dd 30 MeV and low sensitivity
to the accidental background.
A distinctive feature of the detector is a plastic
scintillator, which surrounds BGO crystal and is viewed by
the same photomultiplier tube.
This provides effective protection of the detector
against the charged particle background.
The detector design allows for a compact experimental
setup with a large solid angle of gamma-ray registration.
The simulation of the spectrometer response function
%on the basis of a software package
has been performed and
experimentally verified using GEANT4 program.
The spectrometer was used in a search for the rare muon-catalyzed
fusion (MCF) reaction
dd  4He + 4He +  + 23,8 МэВ
and is designed to study the
pt + 23,8 МэВ
and is designed to study the
pt  4He + 4He +  + 19,8 МэВ + 19,8 МэВ
|
P9-2012-108 (1.773.754)
Averichev A.S. et al.
Results of the 44th and 45th Nuclotron Runs
Total duration of the 44th (November-December 2011) and 45th (February-March
2012) runs was about 2150 h. During about 900 h the beam was used
for experiments in the framework of current program of physical investigations
and for the machine development. Among more important achievements during the 44th run one can mention the
deuteron beam acceleration up to a record energy
of 4 GeV/u and realization of the beam slow extraction at this energy.
During the 45th run the scheduled program of physical
investigations including experiments with the deuteron beam (extracted and at the
internal target) of energy up to 4 GeV/u was fully implemented. During the run the beam
acceleration and slow extraction at 4.5 GeV/u were realized.
|
P15-2012-109 (74.621)
Gangrsky Yu.P. et al.
The Fission Fragment Yields at the Photofission of Actinide Nuclei
The fission fragment yields of isotopes 101Mo, 135I,
135mCs
were measured at the photofission of actinide nuclei 232Th, 238U, 237Np.
These fission fragments have some peculiarities in nuclear
structure or in practical using. The measurements were performed on the
microtron bremsstrahlung at the Flerov Laboratory of Nuclear Reactions, JINR, at
the electron energy 22 MeV. The activation method with an HPGe detector was
used in these measurements of the yields.
|
P18-2012-110 (532.509)
Zorina D.Yu. et al.
Neutron Activation Analysis of Children's Hair from Ongudai District of Altai
In the present study neutron activation analysis was used to determine
short-lived isotopes (Na, Mg, Al, S, Cl, K, Ca, V, Mn, Cu and I) in the hair
of Altai children from four villages in Ongudai district of the Altai
Republic. Data for 54 boys and 132 girls at the age of 7 to 17 were
analyzed. Significantly higher content of sodium, aluminum and chlorine was
observed in the hair of boys over girls. Concentrations of magnesium and
calcium were significantly higher in the hair of girls. Iodine, copper,
manganese and sulfur concentrations in the hair of boys and girls are close
to each other, the differences between the sexes are not significant. Median
concentrations of the studied elements in the hair of boys and girls were,
respectively: Na - 75 and 50; Mg - 49 and 62; Al - 21 and 13; S - 41150 and
39850; Cl - 1020 and 390; Ca - 608 and 973; Mn - 1.1 and 0.82; Cu - 9; I - 0.2  g/g.
It was shown that the high content of calcium and magnesium is
observed in the hair of children living in rural areas with high hardness
and salinity of drinking water. Iodine concentrations in the hair of studied
cohort of children is low, especially in puberty. g/g.
It was shown that the high content of calcium and magnesium is
observed in the hair of children living in rural areas with high hardness
and salinity of drinking water. Iodine concentrations in the hair of studied
cohort of children is low, especially in puberty.
|
P6-2012-111 (104.472)
Rakhimov A.V. et al.
Determination of Distribution Coefficient of Alkaline Earth Elements and Lanthanides in the Cation Exchange
Resin Extractant System
This work is devoted to the experimental determination of distribution coefficients
of the alkaline earth elements and lanthanides in the cation exchange resin - extractant systems.
In some of them high separation factors (F) for Yb-Lu have been obtained. These results can be used
for the group separation of elements in static conditions (adsorption-re-extraction) and for their concentration.
|
17-2012-112
Погосян С. С.
Функции Грина в неравновесных моделях статистической механики
Автореф. дис. ... канд. физ.-мат. наук
(rus)
|
P13-2012-113 (319.574)
Ananiev V.D. et al.
The World's First Pelletized Cold Neutron Moderator
1In July 10, 2012 cold neutrons were generated for the first time with the
unique pelletized neutron moderator CM-202 at the IBR-2 reactor. In this
moderator, small spherical beads of solid mixture of aromatic hydrocarbons -
benzene derivatives - are applied. Aromatic hydrocarbons are known as the
most radiation-resistant hydrogeneous substances and have properties to
moderate slow neutrons effectively. After the start of routine operation of
the new moderator CM-202, the IBR-2 research reactor of the Frank Laboratory
of Neutron Physics will take world's leading position among pulsed neutron
sources for investigation of matter with neutron scattering methods.
|
P3-2012-114 (230.423)
Tsulaia M.I.
Neutron Nuclear Precession - Nuclear Pseudo-Magnetism
This paper contains a complete description of the present state of the
neutron nuclear precession, also known as nuclear pseudo-magnetism, from the
history of its prediction and theoretical description to the present state
of this area of neutron physics. We present different approaches for
describing this phenomenon and also the existing experimental results.
Finally, we describe other physics effects, which need to be observed
experimentally in the future.
|
E13-2012-115 (297.866)
R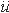 hm A. et al. hm A. et al.
Magnetic Planar Waveguides as Combined Polarizers and
Spin-Flippers for Neutron Microbeams
We propose the waveguides structures which transform an incident unpolarized
neutron beam into a polarized microbeam and can also be used as
spin-flippers by varying the incidence angle on the structure. We describe
optimized structures combining these functions. Such waveguides could be
used for the investigation of one-dimensional magnetic structures and
implemented on any existing fixed wavelength reflectometer.
|
P14-2012-116 (179.664)
Kozhevnikov S.V. et al.
The Use of Polarized Neutron Microbeam for the Investigation
of a Magnetic Microstructure
The use of a neutron microbeam for the investigation of internal magnetic
microstructure is demonstrated experimentally. An object of the
investigation is an amorphous magnetic wire of diameter 190  m with axial and
circular magnetic domains inside it. As a sonde for high spatial resolution
scan, a narrow neutron microbeam of 2.6 m with axial and
circular magnetic domains inside it. As a sonde for high spatial resolution
scan, a narrow neutron microbeam of 2.6  m width is used. This
microbeam was produced by a tri-layer film (a planar waveguide). The method
of investigation is spin precession at transmission of neutron beam through sample. m width is used. This
microbeam was produced by a tri-layer film (a planar waveguide). The method
of investigation is spin precession at transmission of neutron beam through sample.
|
E14-2012-117 (198.262)
Kozhevnikov S.V. et al.
Experimental Determination of Neutron Channeling
Length in a Planar Waveguide
In neutron waveguides the neutron wave is confined inside the guiding layer
of the structure and can escape from the layer edge as a microbeam. The
channeling within the guiding layer is accompanied by an exponential decay
of the neutron wave function density inside the waveguide. Here we report
direct determination of the corresponding decay constant, termed neutron
channeling length. For this, we measured the microbeam intensity as a
function of the length of a neutron absorbing layer of variable length
placed onto the surface of a waveguide structure. Such planar neutron
waveguides transform a conventional neutron beam into an extremely narrow
but slightly divergent microbeam which could be used for the investigation
of nanostructures with submicron spatial resolution.
|
P4-2012-119 (207.143)
Pupyshev V.V.
Scattering of a Slow Quantum Particle by an Axially Symmetrical Short-Range Potential
In the present work, the linear version of the variable phase approach to the potential scattering
is added by a new asymptotic method. This method is adopted for a quantum mechanical analysis and the construction
of explicit low-energy approximations for the partial phase shifts, amplitudes, cross-sections and radial components
of the wave function describing the scattering of a quantum particle by an axially symmetrical short-range potential.
The construction of these approximations is reduced to the solution of the recurrence chain of energy independent
systems. Each system contains two linear first order differential equations.
|
E6-2012-121 (100.582)
Izosimov I.N.
Structure of the Isobar Analog States (IAS), Double Isobar-Analog States (DIAS),
and Configuration States (CS) in Halo Nuclei
Structure of the excited states and resonances with
different isospin quantum numbers in halo-like nuclei is discussed. It is
shown that isobar analog, double isobar-analog, and configuration states
can simultaneously have nn, np, and pp halo components in their wave
functions.
|
9-2012-122
Смирнов В. Л.
Комплексное моделирование компактного циклотрона
Автореф. дис. ... канд. физ.-мат. наук
(rus)
|
P10-2012-123 (2.845.671)
Kozlov G.E.
Study of Clustering Algorithms for Detectors with the Pad Structure
We discuss clustering methods and their application to processing responses
of the detectors with the pad structure that are used in high energy physics experiments.
Hierarchical and iterative methods are described. We discuss their advantages, disadvantages
and applicability to a particular task. Three parameters, accuracy, efficiency and speed, are used
to characterize each method. The Ward and single linkage methods are currently considered to be the
most appropriate choice for our problem. A novel clustering algorithm which takes into account the
peculiarities of our task was developed. Simulation studies showed that the novel algorithm has the best
performance as compared to the standard Ward and single linkage methods.
|
P14-2012-124 (715.781)
Balagurov A.M. et al.
Structural Phase Transition in CuFe2O4 Spinel
Copper ferrite CuFe2O4 shows structural transition at
T  440 440  with a reduction of symmetry of high-temperature
cubic phase
(sp. gr. Fd3m) to tetragonal (sp. gr. I41/amd) and with establishment of
ferrimagnetic structure.
The coexistence of two structural phases of equitable character was observed in a wide temperature range
(~ 40 with a reduction of symmetry of high-temperature
cubic phase
(sp. gr. Fd3m) to tetragonal (sp. gr. I41/amd) and with establishment of
ferrimagnetic structure.
The coexistence of two structural phases of equitable character was observed in a wide temperature range
(~ 40  ) in an experiment using a high resolution neutron diffractometer.
Investigated composition
is a fully inverted spinel in a cubic phase, and the parameter in a tetragonal phase does not exceed several
percent (x = 0.06 ) in an experiment using a high resolution neutron diffractometer.
Investigated composition
is a fully inverted spinel in a cubic phase, and the parameter in a tetragonal phase does not exceed several
percent (x = 0.06 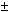 0.04). At the same time the phase emerging at the cooling has the classical quantity
of tetragonal distortion ( 0.04). At the same time the phase emerging at the cooling has the classical quantity
of tetragonal distortion (  1.06). The character of temperature changes of structural parameters
shows that the transition from the cubic phase to tetragonal allows us to conclude that at the heart of it lies
Jahn-Teller distortion of (Cu,Fe)O6 octahedrons but not the boundary migration of copper and iron atoms. 1.06). The character of temperature changes of structural parameters
shows that the transition from the cubic phase to tetragonal allows us to conclude that at the heart of it lies
Jahn-Teller distortion of (Cu,Fe)O6 octahedrons but not the boundary migration of copper and iron atoms.
|
P13-2012-125 (321.623)
Morozov V.A., Morozova N.V.
Investigation of Gas Discharge Processes in PMTs by the Autocorrelation Method
The effect of the potential different at the focusing chamber electrodes of
the FEU-85, FEU-87, and FEU-93 photomultipliers on the intensity of
afterpulses resulting from gas discharge processes is investigated. With
appropriately selected potentials, the number of recorded secondary pulses
can be decreased. Charge distribution spectra are obtained for this sort of
pulses, which gives a qualitative estimate of both the homogeneity of the
charge and mass distribution of residual gases and the ion-electron
emission coefficients.
|
P13-2012-126 (330.833)
Morozov V.A., Morozova N.V.
Specific Features of PMT Secondary Pulse Detection
Specific features of pulse detection by the autocorrelation method are
considered with application to PMT secondary pulses governed by processes of
feedback ion detection or by scintillation time of inorganic scintillators.
It is found that when detecting PMT pulses in the current mode, one should
take into account not only the instrumental dead time of the discriminator,
but also its dynamic dead time.
|
E5-2012-128 (153.715)
Ayryan E.A., Gevorkyan A.S., Sevastyanov L.A.
On the Reduction of Dimensionality of a General Classical Three-Body Problem
The reduction of dimensionality of the general three-body
classical problem is considered in the framework of the ideas of
separation of the internal and external motions of the body system.
Based on the fact that for a Hamiltonian system there exists
equivalence between phase trajectories and geodesic trajectories
on the Riemannian manifold 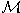 (the Lagrangian surface of the
body system), the classical three-body problem is formulated in the
framework of six ordinary differential equations (ODEs) of the
second order on the tangential bundle of the Lagrange manifold (the Lagrangian surface of the
body system), the classical three-body problem is formulated in the
framework of six ordinary differential equations (ODEs) of the
second order on the tangential bundle of the Lagrange manifold 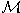 t.
It is shown that in the case when the total
interaction potential of the body system depends on the relative
distances between particles, three out of the six geodesic
equations describing rotations of the
triangle formed by three bodies are solved exactly. Using this fact it was proved that
the general three-body problem can be described in the limits of
three nonlinear ODEs of canonical kind. It is shown that the
reduced problem describes the dynamics of the three-body system on
the scattering plane with consideration of the total angular
momentum of the rotating body triangle. The equations of geodesic
deviations on the manifold t.
It is shown that in the case when the total
interaction potential of the body system depends on the relative
distances between particles, three out of the six geodesic
equations describing rotations of the
triangle formed by three bodies are solved exactly. Using this fact it was proved that
the general three-body problem can be described in the limits of
three nonlinear ODEs of canonical kind. It is shown that the
reduced problem describes the dynamics of the three-body system on
the scattering plane with consideration of the total angular
momentum of the rotating body triangle. The equations of geodesic
deviations on the manifold 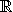 3 (the space of
relative distances between particles) are derived in explicit form.
A system of algebraic equations for finding homographic solutions
of the restricted three-body problem is obtained.
The initial and asymptotic conditions for solution of the classical
scattering problem are found. 3 (the space of
relative distances between particles) are derived in explicit form.
A system of algebraic equations for finding homographic solutions
of the restricted three-body problem is obtained.
The initial and asymptotic conditions for solution of the classical
scattering problem are found.
|
E5-2012-129 (135.923)
Yamaleev R.M.
Solutions of Riccati-Abel Equation in Terms
of Characteristics of General Complex Algebra
The Riccati-Abel differential equation defined as an equation
between the first order derivative and the cubic polynomial is
explored. In the case of constant coefficients this equation is
reduced into an algebraic equation. Method of derivation of a
summation formula for solutions of Riccati-Abel equation is
elaborated. The solutions of the Riccati-Abel equation are
expressed in terms of the characteristic functions of general
complex algebra of the third order.
|
P13-2012-131 (1.420.299)
Pepelyshev Yu.N., Rogov A.D., Tsogtsaikhan Ts.
Statistical Analysis for the Pulse Energy Fluctuations of the IBR-2M Reactor
We present main results of the statistical analysis for the pulse energy
fluctuations at the full cycle of the IBR-2M reactor. The data on the dynamics of the noise
state of the reactor in the cycle are obtained. The frequence ranges, level of the fluctuations
and the possible causes of the fluctuations in the noise energy pulses are presented. Asymmetrical
distribution of energy pulses and non-linear behavior due to fast power feedback have been observed.
It is shown that 4% of the mean square power fluctuations of the full 6% are due to vibrations
of blades of the movable reflectors. The low level of pulse energy fluctuations and stability of their
spectral components confirm the reliability and reactor safety at the average power 2 MW.
|
10-2012-133
Кореньков В. В.
Методология развития научного информационно-вычислительного комплекса в составе глобальной грид-инфраструктуры
Автореф. дис. ... доктора тех. наук
(rus)
|
P10-2012-134 (216.841)
Morkovnikov I.A., Ivankov O.I., Kirilov A.S.
The Program for Measurement Registration at the YuMO Instrument
The work is dedicated to the automation of the registration process of measurements
performed on the IBR-2 instruments. Stored information is intended for those responsible for the instruments,
in order to simplify measurements accounting, provide information search and assist in the preparation of reports.
The general approach to the problem is considered, which in the first phase was implemented on YuMO spectrometer
using Python, PyQt, MySQL.
|
E2-2012-135 (141.577)
Kuraev E.A., Voskresenskaya O.O., Tarasov A.V.
Coulomb Correction to the Screening Angle of the Moli re
Multiple Scattering Theory re
Multiple Scattering Theory
Coulomb correction to the screening angular parameter of the
Moli re multiple
scattering theory is found. Numerical calculations are presented in the range of nuclear charge
4 re multiple
scattering theory is found. Numerical calculations are presented in the range of nuclear charge
4 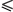 Z Z 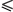 82.
Comparison with the Moli 82.
Comparison with the Moli re result for the screening angle reveals
up to 30% deviation from it for sufficiently heavy elements of the target material. re result for the screening angle reveals
up to 30% deviation from it for sufficiently heavy elements of the target material.
|
E4-2012-136 (103.878)
Severyukhin A.P., Voronov V.V., Borzov I.N., Nguyen Van Giai
Finite Rank Separable Approximation for Skyrme Interactions: Spin-Isospin Excitations
A finite rank separable approximation for the quasiparticle random
phase approximation with the Skyrme interactions is applied for the
case of charge-exchange nuclear modes. The coupling between one-
and two-phonon terms in the wave functions are taken into account.
It has been shown that the approximation reproduces reasonably well
the full charge-exchange RPA results for the spin-dipole
resonances in 132Sn. As an illustration of the method, the
phonon-phonon coupling effect on the 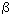 -decay half-life of
78Ni is considered. -decay half-life of
78Ni is considered.
|
1-2012-137
Спасков В. Н.
Измерение сечения дифракционного глубоконеупругого рассеяния с лидирующим протоном в эксперименте H1 на электрон-протонном коллайдере HERA
Автореф. дис. ... канд. физ.-мат. наук
(rus)
|
P10-2012-138 (954.324)
Bednyakov I.V. et al.
Mapping Structures of Proteins and Nucleic Acids
Methods and algorithms for analysis of surfaces of globular and fibrillar proteins,
DNA, and RNA have been developed. These methods of constructing cards of fragments of these objects,
in the cylindrical projection original developed herein, essentially expand possibilities for studying
distribution of charges and a relief of a surface of biological structures. This approach essentially
supplements qualitative characteristics of methods of visualization of biopolymer structures.
|
P10-2012-139 (137.883)
Grokhlina T.I. et al.
Database of Amino Acid-Nucleotide Contacts in the DNA Complexes with Homeodomain Family Proteins
The analysis of amino acid-nucleotide contacts in interfaces of the
protein-DNA complexes, intended to find consistencies in the protein-DNA recognition,
is a complex problem that requires analysis of the physicochemical characteristics of these contacts,
of the positions of the participating amino acids and nucleotides in the chains of the protein and the DNA,
respectively, as well as conservatism of these contacts. Thus, those heterogeneous data should be systematized.
For this purpose we have developed a database of amino acid-nucleotide contacts ANTPC (Amino acid Nucleotide
Type Position Conservation) following the archetypal example of the proteins in the homeodomain family.
We show that it can be used for comparison and classification of interfaces of the protein-DNA complexes.
|
P2-2012-140 (219.666)
Pestov I.B.
Geometric Theory of Fundamental Interactions.
Foundations of Unified Physics
We put forward an idea that regularities of unified physics are in a simple
relation: everything in the concept of space and the concept of space in
everything. With this hypothesis as a ground, a conceptual structure of a
unified geometrical theory of fundamental interactions is created and
deductive derivation of its main equations is produced. The formulated
theory gives solution of the actual problems, provides opportunity to
understand the origin and nature of physical fields, local internal symmetry,
time, energy, spin, charge, confinement, dark energy and dark matter, thus
conforming the existence of new physics in its unity.
|
P2-2012-141 (234.916)
Pestov I.B.
Geometric Theory of Fundamental Interactions. Gravidynamics
In this report a mathematical formulation of fundamental concepts of
unified geometrical theory of fundamental interactions is given. A concept
of momentum of the gravitational field is introduced, equations of
gravidynamics are derived, expressions for kinetic energy, potential energy
and energy flow vector of the gravitational field are found. A most general
form of the law of energy conservation is established, from which it
follows that the hypothetical dark energy is the energy of the gravitational
field. Two exact solutions of the equations of gravidynamics are obtained
and their physical interpretation is given.
|
P2-2012-142 (299.727)
Pestov I.B.
Geometric Theory of Fundamental Interactions. Spinstatics and Spindynamics
The results of the unified geometrical theory of fundamental interactions
that correspond to the physics of microworld are presented and organized
in the form of two subdivisions: Spinstatics and Spindynamics.
It is supposed that regularities of the microworld are in the
relation:
everything in the concept of spin symmetry and the concept of spin symmetry
in everything. It is shown that geometrical and physical nature of the
microworld phenomena or spin one is uncovered in the bipolar structure of
spin symmetry induced by the gravitational potential. A deductive derivation
of equations of Spinstatics and Spindynamics is given. Operators of the
electric charge and neutrino charge are introduced, which give
opportunity to understand real nature of the neutrino. An explanation of
the confinement and quark-lepton symmetry is given. It is established that
the number of the quark-lepton generations is equal to four.
|
P2-2012-143 (187.230)
Pestov I.B.
Geometric Theory of Fundamental Interactions.
Generalized Electromagnetic Field
In this report a theory of a generalized electromagnetic field is
formulated, which is titled so because the singlet state of this field
corresponds to the electromagnetic field. A concept of a ground state of the
generalized electromagnetic field is introduced and deductive derivation of
equations of this field in both geometrical and dynamical form is given.
The general covariant Maxwell equations for the electric and magnetic
fields are derived. A physical interpretation of the theory of the
generalized electromagnetic field is given.
|
4-2012-145
Величков А. И.
Описание кластерной радиоактивности в рамках модели двойной ядерной системы
Автореф. дис. ... канд. физ.-мат. наук
(rus)
|
E19-2012-146 (310.795)
Sivozhelezov V.S. et al.
Electrostatics as a Factor of Biomolecular Recognition in Processes of Transcription and Translation
Electrostatics of DNA, RNA and proteins is mainly determined by the function of these
biomolecules in the processes of transcription and translation, in which the genetic information is
converted into the amino acid sequence of proteins, and then implemented in the spatial structure and
function of these proteins. Herein, we calculated the electrostatic potentials of the promoter regions
of DNA, sigma domain of RNA polymerase and transport RNA, and determined the relationship between the
calculated potentials and function of biomolecules in transcription and translation. We used distributed
computational environment, for which biomolecules are the natural field of application due to their
complexity and high homologous diversity.
|
P1-2012-147 (1.171.954)
Adam I. et al.
The Study of Spatial Distributions of Neutron Capture
and Fission Reactions in Massive Uranium Target Irradiated
by Deuterons with Energies of 1-8 GeV («Quinta» Setup)
This paper presents results of a study of spatial distributions of neutron radiative
capture
and natU fission in the target assembly «Quinta» with a mass of 512 kg of natural metallic uranium
irradiated by deuteron beams from the
accelerator Nuclotron in the energy range from 1 to 8 GeV with the total
number of deuterons on the target ~ 1013 at each energy. From
these data the total numbers of fission reactions in the entire volume of
the uranium target, and the corresponding total numbers of produced 239Pu nuclei were obtained. It was found
that the total numbers of
fission Nf and numbers NPu of accumulated 239Pu nuclei
normalized to one incident deuteron and 1 GeV of its energy remain constant
within experimental error in the studied incident energy range. The values Nf
do not change from adding a lead
blanket to the target assembly
«Quinta», and the values NPu increase by about 55%. Analysis of the
spatial distributions of neutron radiative capture to fission ratios
(spectral indices), the accuracy of which is substantially higher than the
rest of the studied observables (due to the absence of systematic errors of
monitoring of deuteron numbers on the target), indicates softening of the
neutron spectrum at offset from the axis to the periphery of the uranium
target. The degree of this softening increases when adding a lead blanket to
the target assembly.
|
